PGMRA: a web server for (phenotype x genotype) many-to-many relation analysis in GWAS
- PMID: 23761451
- PMCID: PMC3692099
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt496
PGMRA: a web server for (phenotype x genotype) many-to-many relation analysis in GWAS
Abstract
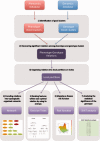
It has been proposed that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) discovered by genome-wide association studies (GWAS) account for only a small fraction of the genetic variation of complex traits in human population. The remaining unexplained variance or missing heritability is thought to be due to marginal effects of many loci with small effects and has eluded attempts to identify its sources. Combination of different studies appears to resolve in part this problem. However, neither individual GWAS nor meta-analytic combinations thereof are helpful for disclosing which genetic variants contribute to explain a particular phenotype. Here, we propose that most of the missing heritability is latent in the GWAS data, which conceals intermediate phenotypes. To uncover such latent information, we propose the PGMRA server that introduces phenomics--the full set of phenotype features of an individual--to identify SNP-set structures in a broader sense, i.e. causally cohesive genotype-phenotype relations. These relations are agnostically identified (without considering disease status of the subjects) and organized in an interpretable fashion. Then, by incorporating a posteriori the subject status within each relation, we can establish the risk surface of a disease in an unbiased mode. This approach complements-instead of replaces-current analysis methods. The server is publically available at http://phop.ugr.es/fenogeno.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multitrait genome association analysis identifies new susceptibility genes for human anthropometric variation in the GCAT cohort.J Med Genet. 2018 Nov;55(11):765-778. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2018-105437. Epub 2018 Aug 30. J Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 30166351 Free PMC article.
-
Integrate multiple traits to detect novel trait-gene association using GWAS summary data with an adaptive test approach.Bioinformatics. 2019 Jul 1;35(13):2251-2257. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty961. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30476000 Free PMC article.
-
Powerful and efficient SNP-set association tests across multiple phenotypes using GWAS summary data.Bioinformatics. 2019 Apr 15;35(8):1366-1372. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty811. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30239606 Free PMC article.
-
The enigma of genetics etiology of atherosclerosis in the post-GWAS era.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2012 Aug;14(4):295-9. doi: 10.1007/s11883-012-0245-0. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2012. PMID: 22437283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene set analysis of SNP data: benefits, challenges, and future directions.Eur J Hum Genet. 2011 Aug;19(8):837-43. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2011.57. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Eur J Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21487444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NMF-mGPU: non-negative matrix factorization on multi-GPU systems.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Feb 13;16:43. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0485-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25887585 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the complex genetics of human character.Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Oct;25(10):2295-2312. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0263-6. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Mol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 30283034 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering Tumour Heterogeneity through PKR and nc886 Analysis in Metastatic Colon Cancer Patients Treated with 5-FU-Based Chemotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 7;12(2):379. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020379. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32045987 Free PMC article.
-
Subgrouping germinal center-derived B-cell lymphomas based on machine learning-deduced DNA methylation modules.Leukemia. 2025 Apr;39(4):967-971. doi: 10.1038/s41375-025-02533-6. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Leukemia. 2025. PMID: 40065077 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
miR-124-3p target genes identify globus pallidus role in suicide ideation recovery in borderline personality disorder.Npj Ment Health Res. 2023;2(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s44184-023-00027-w. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Npj Ment Health Res. 2023. PMID: 37712050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Houle D, Govindaraju DR, Omholt S. Phenomics: the next challenge. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011;11:855–866. - PubMed
-
- Holliday EG, McLean DE, Nyholt DR, Mowry BJ. Susceptibility locus on chromosome 1q23-25 for a schizophrenia subtype resembling deficit schizophrenia identified by latent class analysis. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 2009;66:1058–1067. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources