Short-term bed rest increases TLR4 and IL-6 expression in skeletal muscle of older adults
- PMID: 23761639
- PMCID: PMC3743002
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00072.2013
Short-term bed rest increases TLR4 and IL-6 expression in skeletal muscle of older adults
Abstract
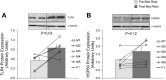
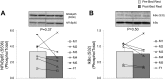
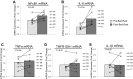
Bed rest induces significant loss of leg lean mass in older adults. Systemic and tissue inflammation also accelerates skeletal muscle loss, but it is unknown whether inflammation is associated to inactivity-induced muscle atrophy in healthy older adults. We determined if short-term bed rest increases toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling and pro-inflammatory markers in older adult skeletal muscle biopsy samples. Six healthy, older adults underwent seven consecutive days of bed rest. Muscle biopsies (vastus lateralis) were taken after an overnight fast before and at the end of bed rest. Serum cytokine expression was measured before and during bed rest. TLR4 signaling and cytokine mRNAs associated with pro- and anti-inflammation and anabolism were measured in muscle biopsy samples using Western blot analysis and qPCR. Participants lost ∼4% leg lean mass with bed rest. We found that after bed rest, muscle levels of TLR4 protein expression and interleukin-6 (IL-6), nuclear factor-κB1, interleukin-10, and 15 mRNA expression were increased after bed rest (P < 0.05). Additionally, the cytokines interferon-γ, and macrophage inflammatory protein-1β, were elevated in serum samples following bed rest (P < 0.05). We conclude that short-term bed rest in older adults modestly increased some pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in muscle samples while systemic changes in pro-inflammatory cytokines were mostly absent. Upregulation of TLR4 protein content suggests that bed rest in older adults increases the capacity to mount an exaggerated, and perhaps unnecessary, inflammatory response in the presence of specific TLR4 ligands, e.g., during acute illness.
Keywords: aging; atrophy; cytokine; hospitalization; physical inactivity.
Figures


References
-
- Argiles JM, Busquets S, Lopez-Soriano FJ. The pivotal role of cytokines in muscle wasting during cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37: 2036–2046, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bosutti A, Malaponte G, Zanetti M, Castellino P, Heer M, Guarnieri G, Biolo G. Calorie restriction modulates inactivity-induced changes in the inflammatory markers C-reactive protein and pentraxin-3. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93: 3226–3229, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Chen YW, Gregory CM, Scarborough MT, Shi R, Walter GA, Vandenborne K. Transcriptional pathways associated with skeletal muscle disuse atrophy in humans. Physiol Genomics 31: 510–520, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

