Distinguishing the effects of convective and diffusive O₂ delivery on VO₂ on-kinetics in skeletal muscle contracting at moderate intensity
- PMID: 23761640
- PMCID: PMC3763029
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00136.2013
Distinguishing the effects of convective and diffusive O₂ delivery on VO₂ on-kinetics in skeletal muscle contracting at moderate intensity
Abstract
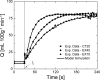
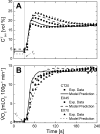
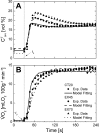
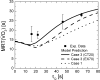
With current techniques, experimental measurements alone cannot characterize the effects of oxygen blood-tissue diffusion on muscle oxygen uptake (Vo₂) kinetics in contracting skeletal muscle. To complement experimental studies, a computational model is used to quantitatively distinguish the contributions of convective oxygen delivery, diffusion into cells, and oxygen utilization to Vo₂ kinetics. The model is validated using previously published experimental Vo₂ kinetics in response to slowed blood flow (Q) on-kinetics in canine muscle (τQ = 20 s, 46 s, and 64 s) [Goodwin ML, Hernández A, Lai N, Cabrera ME, Gladden LB. J Appl Physiol. 112:9-19, 2012]. Distinctive effects of permeability-surface area or diffusive conductance (PS) and Q on Vo₂ kinetics are investigated. Model simulations quantify the relationship between PS and Q, as well as the effects of diffusion associated with PS and Q dynamics on the mean response time of Vo₂. The model indicates that PS and Q are linearly related and that PS increases more with Q when convective delivery is limited by slower Q dynamics. Simulations predict that neither oxygen convective nor diffusive delivery are limiting Vo₂ kinetics in the isolated canine gastrocnemius preparation under normal spontaneous conditions during transitions from rest to moderate (submaximal) energy demand, although both operate close to the tipping point.
Keywords: diffusion; modeling; permeability-surface area; tipping point; transport.
Figures



References
-
- Bauer TA, Brass EP, Hiatt WR. Impaired muscle oxygen use at onset of exercise in peripheral arterial disease. J Vasc Surg 40: 488–493, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Caldwell JH, Martin GV, Raymond GM, Bassingthwaighte JB. Regional myocardial flow and capillary permeability-surface area products are nearly proportional. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 267: H654–H666, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Cousineau D, Rose CP, Goresky CA. Plasma expansion effect on cardiac capillary and adrenergic exchange in intact dogs. J Appl Physiol 60: 147–153, 1986 - PubMed
-
- Cousineau D, Rose CP, Lamoureux D, Goresky CA. Changes in cardiac transcapillary exchange with metabolic coronary vasodilation in the intact dog. Circ Res 53: 719–730, 1983 - PubMed
-
- Cousineau DF, Goresky CA, Rose CP, Schwab AJ. Cardiac microcirculatory effects of beta-adrenergic blockade during sympathetic stimulation. Circ Res 68: 997–1006, 1991 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

