Novel role of ouabain as a cystogenic factor in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
- PMID: 23761677
- PMCID: PMC3761286
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00248.2013
Novel role of ouabain as a cystogenic factor in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
Abstract
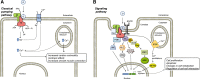
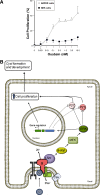
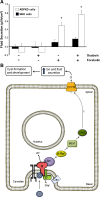
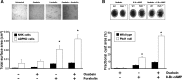
The classic role of the Na-K-ATPase is that of a primary active transporter that utilizes cell energy to establish and maintain transmembrane Na(+) and K(+) gradients to preserve cell osmotic stability, support cell excitability, and drive secondary active transport. Recent studies have revealed that Na-K-ATPase located within cholesterol-containing lipid rafts serves as a receptor for cardiotonic steroids, including ouabain. Traditionally, ouabain was viewed as a toxin produced only in plants, and it was used in relatively high concentrations to experimentally block the pumping action of the Na-K-ATPase. However, the new and unexpected role of the Na-K-ATPase as a signal transducer revealed a novel facet for ouabain in the regulation of a myriad of cell functions, including cell proliferation, hypertrophy, apoptosis, mobility, and metabolism. The seminal discovery that ouabain is endogenously produced in mammals and circulates in plasma has fueled the interest in this endogenous molecule as a potentially important hormone in normal physiology and disease. In this article, we review the role of the Na-K-ATPase as an ion transporter in the kidney, the experimental evidence for ouabain as a circulating hormone, the function of the Na-K-ATPase as a signal transducer that mediates ouabain's effects, and novel results for ouabain-induced Na-K-ATPase signaling in cystogenesis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Keywords: Na-K-ATPase signalosome; cardiotonic steroids; polycystic kidney disease.
Figures

References
-
- . Polycystic kidney disease: the complete structure of the PKD1 gene, and its protein. The International Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium. Cell 81: 289–298, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Abramowitz J, Dai C, Hirschi KK, Dmitrieva RI, Doris PA, Liu L, Allen JC. Ouabain- and marinobufagenin-induced proliferation of human umbilical vein smooth muscle cells and a rat vascular smooth muscle cell line, A7r5. Circulation 108: 3048–3053, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Agrawal AA, Petschenka G, Bingham RA, Weber MG, Rasmann S. Toxic cardenolides: chemical ecology and coevolution of specialized plant-herbivore interactions. New Phytol 194: 28–45, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Aizman O, Aperia A. Na,K-ATPase as a signal transducer. Ann NY Acad Sci 986: 489–496, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

