Multiscale segmentation of the skull in MR images for MRI-based attenuation correction of combined MR/PET
- PMID: 23761683
- PMCID: PMC3822115
- DOI: 10.1136/amiajnl-2012-001544
Multiscale segmentation of the skull in MR images for MRI-based attenuation correction of combined MR/PET
Abstract
Background and objective: Combined magnetic resonance/positron emission tomography (MR/PET) is a relatively new, hybrid imaging modality. MR-based attenuation correction often requires segmentation of the bone on MR images. In this study, we present an automatic segmentation method for the skull on MR images for attenuation correction in brain MR/PET applications.
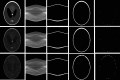
Materials and methods: Our method transforms T1-weighted MR images to the Radon domain and then detects the features of the skull image. In the Radon domain we use a bilateral filter to construct a multiscale image series. For the repeated convolution we increase the spatial smoothing in each scale and make the width of the spatial and range Gaussian function doubled in each scale. Two filters with different kernels along the vertical direction are applied along the scales from the coarse to fine levels. The results from a coarse scale give a mask for the next fine scale and supervise the segmentation in the next fine scale. The use of the multiscale bilateral filtering scheme is to improve the robustness of the method for noise MR images. After combining the two filtered sinograms, the reciprocal binary sinogram of the skull is obtained for the reconstruction of the skull image.
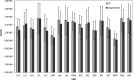
Results: This method has been tested with brain phantom data, simulated brain data, and real MRI data. For real MRI data the Dice overlap ratios are 92.2%±1.9% between our segmentation and manual segmentation.
Conclusions: The multiscale segmentation method is robust and accurate and can be used for MRI-based attenuation correction in combined MR/PET.
Keywords: Attenuation correction; Combined MR/PET; Image segmentation; Multimodality Imaging; Radon transform; multiscale bilateral filter.
Figures





References
-
- Sauter AW, Wehrl HF, Kolb A, et al. Combined PET/MRI: one step further in multimodality imaging. Trends Mol Med 2010;16:508–15 - PubMed
-
- Zaidi H, Montandon ML, Slosman DO. Magnetic resonance imaging-guided attenuation and scatter corrections in three-dimensional brain positron emission tomography. Med Phys 2003;30:937–48 - PubMed
-
- Schulz V, Torres-Espallardo I, Renisch S, et al. Automatic, three-segment, MR-based attenuation correction for whole-body PET/MR data. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2011;38:138–52 - PubMed
-
- Kops ER, Wagenknecht G, Scheins J, et al. Attenuation correction in MR-PET scanners with segmented T1-weighted MR images. In: Yu B, ed. 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record; Vol 1–5, 2009:2530–3
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

