Pre-mRNA processing factors meet the DNA damage response
- PMID: 23761808
- PMCID: PMC3674313
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00102
Pre-mRNA processing factors meet the DNA damage response
Abstract
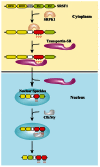
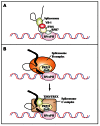
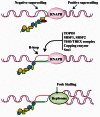
It is well-known that DNA-damaging agents induce genome instability, but only recently have we begun to appreciate that chromosomes are fragile per se and frequently subject to DNA breakage. DNA replication further magnifies such fragility, because it leads to accumulation of single-stranded DNA. Recent findings suggest that chromosome fragility is similarly increased during transcription. Transcripts produced by RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) are subject to multiple processing steps, including maturation of 5' and 3' ends and splicing, followed by transport to the cytoplasm. RNA maturation starts on nascent transcripts and is mediated by a number of diverse proteins and ribonucleoprotein particles some of which are recruited cotranscriptionally through interactions with the carboxy-terminal domain of RNAPII. This coupling is thought to maximize efficiency of pre-mRNA maturation and directly impacts the choice of alternative splice sites. Mounting evidence suggests that lack of coordination among different RNA maturation steps, by perturbing the interaction of nascent transcripts with the DNA template, has deleterious effects on genome stability. Thus, in the absence of proper surveillance mechanisms, transcription could be a major source of DNA damage in cancer. Recent high-throughput screenings in human cells and budding yeast have identified several factors implicated in RNA metabolism that are targets of DNA damage checkpoint kinases: ATM (ataxia telangiectasia mutated) and ATR (ATM-Rad3 related) (Tel1 and Mec1 in budding yeast, respectively). Moreover, inactivation of various RNA processing factors induces accumulation of γH2AX foci, an early sign of DNA damage. Thus, a complex network is emerging that links DNA repair and RNA metabolism. In this review we provide a comprehensive overview of the role played by pre-mRNA processing factors in the cell response to DNA damage and in the maintenance of genome stability.
Keywords: DNA damage response; RNA binding proteins; checkpoint kinases; pre-mRNA processing; splicing.
Figures

References
-
- Baranello L., Bertozzi D., Fogli M. V., Pommier Y., Capranico G. (2010). DNA topoisomerase I inhibition by camptothecin induces escape of RNA polymerase II from promoter-proximal pause site, antisense transcription and histone acetylation at the human HIF-1alpha gene locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 38 159–171 10.1093/nar/gkp817 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

