A novel brain penetrant NPS receptor antagonist, NCGC00185684, blocks alcohol-induced ERK-phosphorylation in the central amygdala and decreases operant alcohol self-administration in rats
- PMID: 23761908
- PMCID: PMC3682378
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4742-12.2013
A novel brain penetrant NPS receptor antagonist, NCGC00185684, blocks alcohol-induced ERK-phosphorylation in the central amygdala and decreases operant alcohol self-administration in rats
Abstract
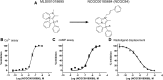
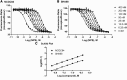
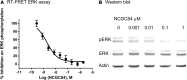
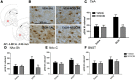
The Neuropeptide S receptor, a Gs/Gq-coupled GPCR expressed in brain regions involved in mediating drug reward, has recently emerged as a candidate therapeutic target in addictive disorders. Here, we describe the in vitro and in vivo pharmacology of a novel, selective and brain penetrant NPSR antagonist with nanomolar affinity for the NPSR, NCGC00185684. In vitro, NCGC00185684 shows biased antagonist properties, and preferentially blocks ERK-phosphorylation over intracellular cAMP or calcium responses to NPS. In vivo, systemic NCGC00185684 blocks alcohol-induced ERK-phosphorylation in the rat central amygdala, a region involved in regulation of alcohol intake. NCGC00185684 also decreases operant alcohol self-administration, and lowers motivation for alcohol reward as measured using progressive ratio responding. These effects are behaviorally specific, in that they are observed at doses that do not influence locomotor activity or reinstatement responding following extinction. Together, these data provide an initial validation of the NPSR as a therapeutic target in alcoholism.
Figures



References
-
- Badia-Elder NE, Henderson AN, Bertholomey ML, Dodge NC, Stewart RB. The effects of neuropeptide S on ethanol drinking and other related behaviors in alcohol-preferring and -nonpreferring rats. Alcoholism, clinical and experimental research. 2008;32:1380–1387. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00713.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Camarda V, Rizzi A, Ruzza C, Zucchini S, Marzola G, Marzola E, Guerrini R, Salvadori S, Reinscheid RK, Regoli D, Cal ò G. In vitro and in vivo pharmacological characterization of the neuropeptide s receptor antagonist [D-Cys(tBu)5]neuropeptide S. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;328:549–555. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.143867. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
