An update of teriflunomide for treatment of multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 23761970
- PMCID: PMC3673963
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S30947
An update of teriflunomide for treatment of multiple sclerosis
Abstract
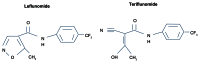
There are a number of oral agents emerging as potential disease-modifying agents in multiple sclerosis (MS). Among these investigational agents, teriflunomide has shown promise in large, multicenter, phase III clinical trials with respect to safety and efficacy in relapsing MS patients, and is the latest disease-modifying agent approved for use in MS patients in the United States. This review will summarize teriflunomide's historical development, clinical pharmacology, studies in animals, clinical trials, and safety data, and will end with a discussion of the role of teriflunomide in MS in the context of existing treatment options.
Keywords: clinical trials; multiple sclerosis; review; teriflunomide.
Figures


References
-
- Marriott JJ, O’Connor PW. Emerging therapies in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2010;5:179–188. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett RR, Schleyerbach R. Immunopharmacological profile of a novel isoxazol derivative, HWA 486, with potential antirheumatic activity – I. Disease modifying action on adjuvant arthritis of the rat. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1985;7:7–18. - PubMed
-
- Korn T, Magnus T, Toyka K, Jung S. Modulation of effector cell functions in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by leflunomide – mechanisms independent of pyrimidine depletion. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;76:950–960. - PubMed
-
- Posevitz V. Teriflunomide selectively suppresses antigen induced T cell expansion in a TCR avidity dependent fashion. Paper presented at the 28th Congress of the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ECTRIMS); October 10–13, 2012; Lyon, France.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

