Targeted therapies in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 23761989
- PMCID: PMC3667684
- DOI: 10.4137/CMO.S7633
Targeted therapies in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common liver cancer and the third leading cause of cancer death. It has been a major worldwide health problem with more new cases being diagnosed each year. The current available therapies for patients with advanced HCC are extremely limited. Therefore, it is of great clinical interests to develop more effective therapies for systemic treatment of advanced HCC. Several promising target-based drugs have been tested in a number of clinical trials. One breakthrough of these efforts is the approved clinical use of sorafenib in patients with advanced HCC. Targeted therapies are becoming an attractive option for the treatment of advanced HCC. In this review, we summarize the most recent progress in clinical targeted treatments of advanced HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); signaling pathway; sorafenib; targeted therapy; tumor inhibitor.
Figures
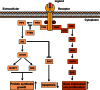
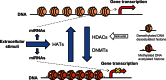
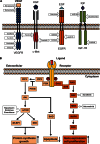
References
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis C in the United States. Hepatology. 2002;36(5 Suppl 1):S74–83. - PubMed
-
- Lin CL, Kao JH. Hepatitis B viral factors and clinical outcomes of chronic hepatitis B. J Biomedl Sci. 2008;15(2):137–45. - PubMed
-
- Lau WY, Lai EC. Hepatocellular carcinoma: current management and recent advances. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2008;7(3):237–57. - PubMed
-
- Cabrera R, Nelson DR. Review article: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;31(4):461–76. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB, Tran T, Everhart JE. Diabetes increases the risk of chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(2):460–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

