Shikonin Suppresses Human T Lymphocyte Activation through Inhibition of IKK β Activity and JNK Phosphorylation
- PMID: 23762128
- PMCID: PMC3670545
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/379536
Shikonin Suppresses Human T Lymphocyte Activation through Inhibition of IKK β Activity and JNK Phosphorylation
Abstract
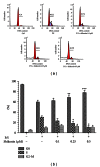
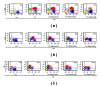
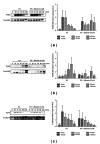
The key role of T cells has been elaborated in mediating immune responses and pathogenesis of human inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. In the current study the effect of shikonin, a compound isolated from a medicinal plant, on inhibition of T-cell activation was firstly examined by using primary human T lymphocytes isolated from buffy coat. Results showed that shikonin dose dependently suppressed T-cell proliferation, IL-2 and IFN- γ secretion, CD69 and CD25 expression, as well as cell cycle arrest activated by costimulation of PMA/ionomycin or OKT-3/CD28 monoclonal antibodies. Moreover, these inhibitory responses mediated by shikonin were found to be associated with suppression of the NF- κ B signaling pathway via inhibition of the IKK α / β phosphorylation, I κ B- α phosphorylation and degradation, and NF- κ B nuclear translocation by directly decreasing IKK β activity. Moreover, shikonin suppressed JNK phosphorylation in the MAPKs pathway of T cells. In this connection, we conclude that shikonin could suppress T lymphocyte activation through suppressing IKK β activity and JNK signaling, which suggests that shikonin is valuable for further investigation as a potential immunosuppressive agent.
Figures




References
-
- Chen X, Yang L, Oppenheim JJ, Zack Howard OM. Cellular pharmacology studies of shikonin derivatives. Phytotherapy Research. 2002;16(3):199–209. - PubMed
-
- Wu Z, Wu L, Li L, Tashiro SI, Onodera S, Ikejima T. p53-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induced by shikonin via a caspase-9-dependent mechanism in human malignant melanoma A375-S2 cells. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences. 2004;94(2):166–176. - PubMed
-
- Wang JP, Raung SL, Chang LC, Kuo SC. Inhibition of hind-paw edema and cutaneous vascular plasma extravasation in mice by acetylshikonin. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1995;272(1):87–95. - PubMed
-
- Mao X, Rong Yu C, Hua Li W, Xin Li W. Induction of apoptosis by shikonin through a ROS/JNK-mediated process in Bcr/Abl-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) cells. Cell Research. 2008;18(8):879–888. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

