A Systems Biology Approach to Characterize Biomarkers for Blood Stasis Syndrome of Unstable Angina Patients by Integrating MicroRNA and Messenger RNA Expression Profiling
- PMID: 23762142
- PMCID: PMC3666437
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/510208
A Systems Biology Approach to Characterize Biomarkers for Blood Stasis Syndrome of Unstable Angina Patients by Integrating MicroRNA and Messenger RNA Expression Profiling
Abstract
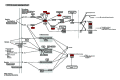
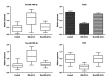
Blood stasis syndrome (BSS) has been considered to be the major type of syndromes in unstable angina (UA) patients. The aim of this study was to find the systems biology-based microRNA (miRNA) and mRNA expression biomarkers for BSS of UA. We identified 1081 mRNAs and 25 miRNAs differentially expressed between BSS of UA patients and healthy controls by microarrays. We used DAVID, miRTrail, and the protein-protein interactions method to explore the related pathways and networks of differentially expressed miRNAs and mRNAs. By combining the results of pathways and networks, we found that the upregulation of miR-146b-5p may induce the downregulation of CALR to attenuate inflammation and the upregulation of miR-199a-5p may induce the downregulation of TP53 to inhibit apoptosis in BSS of UA patients. The expression patterns of miR-146b-5p, miR-199a-5p, CALR, and TP53 were confirmed by qRT-PCR in an independent validation cohort including BBS of UA patients, non-BBS of UA patients, and healthy controls. miR-146b-5p, miR-199a-5p, CALR, and TP53 could be significant biomarkers of BSS of UA patients. The systems biology-based miRNA and mRNA expression biomarkers for the BSS of UA may be helpful for the further stratification of UA patients when deciding on interventions or clinical trials.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Identification of more objective biomarkers for Blood-Stasis syndrome diagnosis.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Sep 22;16(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1349-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27660006 Free PMC article.
-
Nourin-Dependent miR-137 and miR-106b: Novel Early Inflammatory Diagnostic Biomarkers for Unstable Angina Patients.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 28;11(3):368. doi: 10.3390/biom11030368. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33670982 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic potential of plasmatic MicroRNA signatures in stable and unstable angina.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 15;8(11):e80345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080345. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24260372 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression profiles in the left atrium of patients with nonvalvular paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: Role of miR-146b-5p in atrial fibrosis.Heart Rhythm. 2015 May;12(5):1018-26. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.01.026. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Heart Rhythm. 2015. PMID: 25617731
-
Biomedical mechanisms of blood stasis syndrome of coronary heart disease by systems biology approaches.Chin J Integr Med. 2014 Mar;20(3):163-9. doi: 10.1007/s11655-013-1461-3. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Chin J Integr Med. 2014. PMID: 23918233 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the Molecular Mechanism of Quercetin Protecting against Podocyte Injury to Attenuate Diabetic Nephropathy through Network Pharmacology, MicroarrayData Analysis, and Molecular Docking.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 16;2022:7291434. doi: 10.1155/2022/7291434. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35615688 Free PMC article.
-
mastR: an R package for automated identification of tissue-specific gene signatures in multi-group differential expression analysis.Bioinformatics. 2025 Mar 4;41(3):btaf114. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf114. Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40098239 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated RBC senescence as a novel pathologic mechanism of blood stasis syndrome in traditional East Asian medicine.Am J Transl Res. 2015 Mar 15;7(3):422-9. eCollection 2015. Am J Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 26045884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep disruption and the sequelae associated with traumatic brain injury.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Aug;55:68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.04.010. Epub 2015 May 6. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015. PMID: 25956251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of more objective biomarkers for Blood-Stasis syndrome diagnosis.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Sep 22;16(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1349-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27660006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wright RS, Anderson JL, Adams CD, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA focused update of the guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/ Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (updating the 2007 guideline): a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2011;123(18):2022–2060. - PubMed
-
- Braunwald E. Unstable angina and non-ST elevation myocardial infarction. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2012;185(9):924–932. - PubMed
-
- Kuzniatsova N, Shantsila E, Blann A, Lip GYH. A contemporary viewpoint on ‘aspirin resistance’. Annals of Medicine. 2012;44(8):773–783. - PubMed
-
- Zhang YC, Lu BJ, Zhao MH, Rong YZ, Chen RM. Effect of Shengmai injection on vascular endothelial and heart functions in patients with coronary heart disease complicated with diabetes mellitus. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine. 2008;14(4):281–285. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

