Evaluation of the Wound Healing Potential of Resina Draconis (Dracaena cochinchinensis) in Animal Models
- PMID: 23762154
- PMCID: PMC3670512
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/709865
Evaluation of the Wound Healing Potential of Resina Draconis (Dracaena cochinchinensis) in Animal Models
Abstract
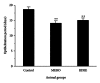
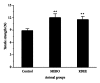
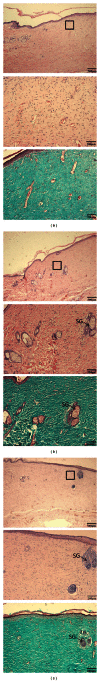
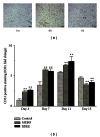
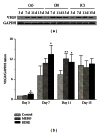
Resina Draconis (RD) is a type of dragon's blood resin obtained from Dracaena cochinchinensis (Lour.) S.C. Chen (Yunnan, China). It has been used as a medicine since ancient times by many cultures. The ethanolic extract of Resina Draconis (RDEE) was evaluated for its wound-healing activity using excision and incision wound models in rats. Group I, the control group, was treated with ointment base. Group II, which served as a reference standard, was treated with moist exposed burn ointment (MEBO). Group III was treated with RDEE. The parameters observed were percentage of wound contraction, epithelialization period, tensile strength, histopathological studies, microvessel density (MVD), and the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor- β 1 (TGF- β 1). The group treated with RDEE showed significantly better wound contraction and better skin-breaking strength as compared with the control group. The results of histopathological examination, MVD, and the expression levels of growth factors supported the outcome of the wound models as well. The present study provided a scientific rationale for the traditional use of RD in the management of wounds.
Figures



References
-
- Akkol EK, Koca U, Peşin I, Yilmazer D, Toker G, Yeşilada E. Exploring the wound healing activity of Arnebia densiflora (Nordm.) Ledeb. by in vivo models. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2009;124(1):137–141. - PubMed
-
- Süntar IP, Akkol EK, Yilmazer D, et al. Investigations on the in vivo wound healing potential of Hypericum perforatum L. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2010;127(2):468–477. - PubMed
-
- Fronza M, Heinzmann B, Hamburger M, Laufer S, Merfort I. Determination of the wound healing effect of Calendula extracts using the scratch assay with 3T3 fibroblasts. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2009;126(3):463–467. - PubMed
-
- Cai X, Xu Z. Studies on the plant origin of Chinese Dragon’s blood. Acta Botanica Yunnanica. 1979;1:1–9.
-
- Committee CP. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. Vol. 88. Beijing, China: China Chemical Industry Press; 2005.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

