Involvement of oxidative stress in occurrence of relapses in multiple sclerosis: the spectrum of oxidatively modified serum proteins detected by proteomics and redox proteomics analysis
- PMID: 23762311
- PMCID: PMC3676399
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065184
Involvement of oxidative stress in occurrence of relapses in multiple sclerosis: the spectrum of oxidatively modified serum proteins detected by proteomics and redox proteomics analysis
Abstract
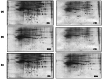
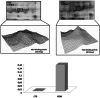
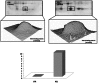
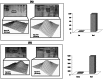
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system. Several evidences suggest that MS can be considered a multi-factorial disease in which both genetics and environmental factors are involved. Among proposed candidates, growing results support the involvement of oxidative stress (OS) in MS pathology. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of OS in event of exacerbations in MS on serum of relapsing-remitting (RR-MS) patients, either in relapsing or remitting phase, with respect to serum from healthy subjects. We applied proteomics and redox proteomics approaches to identify differently expressed and oxidatively modified proteins in the low-abundant serum protein fraction. Among differently expressed proteins ceruloplasmin, antithrombin III, clusterin, apolipoprotein E, and complement C3, were up-regulated in MS patients compared with healthy controls. Further by redox proteomics, vitamin D-binding protein showed a progressive trend of oxidation from remission to relapse, respect with controls. Similarly, the increase of oxidation of apolipoprotein A-IV confirmed that levels of OS are elevated with the progression of the disease. Our findings support the involvement of OS in MS and suggest that dysfunction of target proteins occurs upon oxidative damage and correlates with the pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Polman CH, Reingold SC, Edan G, Filippi M, Hartung H-P, et al. (2005) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the “McDonald Criteria”. Annals of Neurology 58: 840–846. - PubMed
-
- Compston A, Coles A (2008) Multiple sclerosis. The Lancet 372: 1502–1517. - PubMed
-
- Silber E, Sharief MK (1999) Axonal degeneration in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 170: 11–18. - PubMed
-
- Trapp BD, Ransohoff R, Rudick R (1999) Axonal pathology in multiple sclerosis: relationship to neurologic disability. Curr Opin Neurol 12: 295–302. - PubMed
-
- Gonsette RE (2008) Neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis: The role of oxidative stress and excitotoxicity. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 274: 48–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

