Beneficial effects of the activation of the angiotensin-(1-7) MAS receptor in a murine model of adriamycin-induced nephropathy
- PMID: 23762470
- PMCID: PMC3676359
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066082
Beneficial effects of the activation of the angiotensin-(1-7) MAS receptor in a murine model of adriamycin-induced nephropathy
Abstract
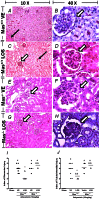
Angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)] is a biologically active heptapeptide that may counterbalance the physiological actions of angiotensin II (Ang II) within the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Here, we evaluated whether activation of the Mas receptor with the oral agonist, AVE 0991, would have renoprotective effects in a model of adriamycin (ADR)-induced nephropathy. We also evaluated whether the Mas receptor contributed for the protective effects of treatment with AT1 receptor blockers. ADR (10 mg/kg) induced significant renal injury and dysfunction that was maximal at day 14 after injection. Treatment with the Mas receptor agonist AVE 0991 improved renal function parameters, reduced urinary protein loss and attenuated histological changes. Renoprotection was associated with reduction in urinary levels of TGF-β. Similar renoprotection was observed after treatment with the AT1 receptor antagonist, Losartan. AT1 and Mas receptor mRNA levels dropped after ADR administration and treatment with losartan reestablished the expression of Mas receptor and increased the expression of ACE2. ADR-induced nephropathy was similar in wild type (Mas(+/+) ) and Mas knockout (Mas (-/-)) mice, suggesting there was no endogenous role for Mas receptor activation. However, treatment with Losartan was able to reduce renal injury only in Mas(+/+) , but not in Mas (-/-) mice. Therefore, these findings suggest that exogenous activation of the Mas receptor protects from ADR-induced nephropathy and contributes to the beneficial effects of AT1 receptor blockade. Medications which target specifically the ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis may offer new therapeutic opportunities to treat human nephropathies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
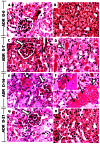
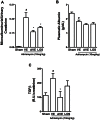
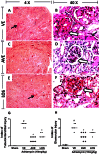
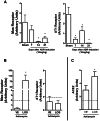
References
-
- Benter IF, Ferrario CM, Morris M, Diz DI (1995) Antihypertensive actions of angiotensin-(1–7) in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol 269: H313–319. - PubMed
-
- Santos RA, Ferreira AJ, Simoes e Silva AC (2008) Recent advances in the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-angiotensin(1–7)-Mas axis. Exp Physiol 93: 519–527. - PubMed
-
- Casas JP, Chua W, Loukogeorgakis S, Vallance P, Smeeth L, et al. (2005) Effect of inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system and other antihypertensive drugs on renal outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 366: 2026–2033. - PubMed
-
- Ji Z, Huang C, Liang C, Chen B, Chen S, et al. (2005) Protective effects of blocking renin-angiotensin system on the progression of renal injury in glomerulosclerosis. Cell Mol Immunol 2: 150–154. - PubMed
-
- Mihailovic-Stanojevic N, Jovovic D, Miloradovic Z, Grujic-Milanovic J, Jerkic M, et al. (2009) Reduced progression of adriamycin nephropathy in spontaneously hypertensive rats treated by losartan. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24: 1142–1150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

