AP1 transcription factors in epidermal differentiation and skin cancer
- PMID: 23762562
- PMCID: PMC3676924
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/537028
AP1 transcription factors in epidermal differentiation and skin cancer
Abstract
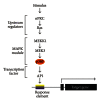
AP1 (jun/fos) transcription factors (c-jun, junB, junD, c-fos, FosB, Fra-1, and Fra-2) are key regulators of epidermal keratinocyte survival and differentiation and important drivers of cancer development. Understanding the role of these factors in epidermis is complicated by the fact that each protein is expressed, at different levels, in multiple cells layers in differentiating epidermis, and because AP1 transcription factors regulate competing processes (i.e., proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation). Various in vivo genetic approaches have been used to study these proteins including targeted and conditional knockdown, overexpression, and expression of dominant-negative inactivating AP1 transcription factors in epidermis. Taken together, these studies suggest that individual AP1 transcription factors have different functions in the epidermis and in cancer development and that altering AP1 transcription factor function in the basal versus suprabasal layers differentially influences the epidermal differentiation response and disease and cancer development.
Figures
References
-
- Cotsarelis G. Epithelial stem cells: a folliculocentric view. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2006;126(7):1459–1468. - PubMed
-
- Kalinin AE, Kajava AV, Steinert PM. Epithelial barrier function: assembly and structural features of the cornified cell envelope. BioEssays. 2002;24(9):789–800. - PubMed
-
- Steinert PM. A model for the hierarchical structure of the human epidermal cornified cell envelope. Cell Death and Differentiation. 1995;2(1):33–40. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

