Diagnosis and management of giant hepatic hemangioma: the usefulness of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography
- PMID: 23762570
- PMCID: PMC3670574
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/802180
Diagnosis and management of giant hepatic hemangioma: the usefulness of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography
Abstract
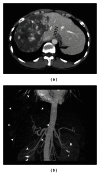
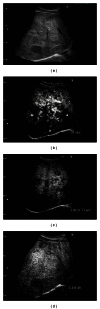
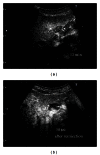
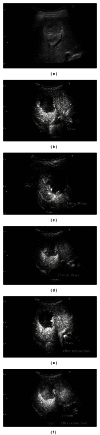
Giant hepatic hemangiomas, though often asymptomatic, may require intervention if rapid growth occurs. The imaging studies including the computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and ultrasonography, and so on are effective for the diagnosis and the management of this tumor; however, due to its size and various patterns of these studies, we need to carefully consider the therapeutic methods. Compared to the cost needed for these modalities, recently developed and approved Perflubutane- (Sonazoid-) based contrast agent enhanced ultrasonography is reasonable and safe. The major advantage is the real-time observation of the vascular structure and function of the Kupffer cells. By this procedure, we can carefully follow the tumor growth or character change in a hemangioma and decide the timing of therapeutic intervention, since abdominal pain, abdominal mass, consumptive coagulopathy, and hemangioma growth are the signs for the therapeutic intervention. We reviewed recent reports about Sonazoid-based enhancement and also showed the representative images collected in our department. This is the first review showing the detailed findings of the giant hemangiomas using Perflubutane (Sonazoid). This review will help the physician in making the decision, and we hope that Sonazoid will gain widespread acceptance in the near future.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kupffer-phase findings of hepatic hemangiomas in contrast-enhanced ultrasound with sonazoid.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2014 Jun;40(6):1089-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2013.12.019. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24556559
-
Spontaneous rupture of hepatic hemangiomas: A review of the literature.World J Hepatol. 2010 Dec 27;2(12):428-33. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i12.428. World J Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 21191518 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of hepatic hemangioma by parametric imaging using sonazoid-enhanced US.Hepatogastroenterology. 2011 Sep-Oct;58(110-111):1431-5. doi: 10.5754/hge10006. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Hepatogastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21940325
-
Management of giant liver hemangiomas: an update.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Mar;7(3):263-8. doi: 10.1586/egh.13.10. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23445235 Review.
-
What is changing in indications and treatment of hepatic hemangiomas. A review.Ann Hepatol. 2014 Jul-Aug;13(4):327-39. Ann Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24927603 Review.
Cited by
-
One stop shop approach for the diagnosis of liver hemangioma.World J Hepatol. 2021 Dec 27;13(12):1892-1908. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i12.1892. World J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 35069996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A large pericardial cystic lymphangioma presenting as acute-onset respiratory distress in a child: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2022 Oct 31;16(1):397. doi: 10.1186/s13256-022-03576-4. J Med Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36316785 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic hemangioma -review-.J Med Life. 2015;8 Spec Issue(Spec Issue):4-11. J Med Life. 2015. PMID: 26361504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surgical management of giant hepatic hemangioma: A 10-year single center experience.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021 Jul 6;69:102542. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102542. eCollection 2021 Sep. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34457247 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Predictive Factors for Transarterial Bleomycin-Lipiodol Embolization Success in Treating Giant Hepatic Hemangiomas.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 26;17(1):42. doi: 10.3390/cancers17010042. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39796672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mungovan JA, Cronan JJ, Vacarro J. Hepatic cavernous hemangiomas: lack of enlargement over time. Radiology. 1994;191(1):111–113. - PubMed
-
- Sinanan MN, Marchioro T. Management of cavernous hemangioma of the liver. American Journal of Surgery. 1989;157(5):519–522. - PubMed
-
- Belli L, De Carlis L, Beati C, Rondinara G, Sansalone V, Brambilla G. Surgical treatment of symptomatic giant hemangiomas of the liver. Surgery Gynecology and Obstetrics. 1992;174(6):474–478. - PubMed
-
- Dietrich CF, Mertens JC, Braden B, Schuessler G, Ott M, Ignee A. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of histologically proven liver hemangiomas. Hepatology. 2007;45(5):1139–1145. - PubMed
-
- Bartolotta TV, Taibbi A, Midiri M, Lagalla R. Focal liver lesions: contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Abdominal Imaging. 2009;34(2):193–209. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

