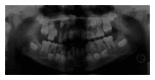
Dentinal dysplasia type I: a case report with a 6-year followup
- PMID: 23762649
- PMCID: PMC3666433
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/659084
Dentinal dysplasia type I: a case report with a 6-year followup
Abstract
Introduction. Dentin dysplasia is a rare disturbance of dentin formation characterized by normal enamel but atypical dentin formation with abnormal pulpal morphology that is inherited as an autosomal pulpal morphology. Case Presentation. A 7-year-old female who had problems in chewing function was referred to Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Department at the Faculty of Dentistry in Ondokuz Mayıs University. In the radiographic examination, it was determined that some of the unerupted permanent teeth of the patient had short, blunted, and malformed roots with obliterated pulp chambers, although the bone below the teeth showed well-defined margins. This unusual case of generalized short roots presents a case demonstrating both classic and atypical features of dentinal dysplasia type I (DDI) in the mixed and permanent dentitions. Conclusion. There are still many issues in the diagnosis and management of patients with dentin dysplasia. Early diagnosis, clinical and radiographic findings, as well as treatment of this condition and the initiation of effective preventive strategies may help prevent or delay loss of dentition.
Figures
References
-
- Kim JW, Simmer JP. Hereditary dentin defects. Journal of Dental Research. 2007;86(5):392–399. - PubMed
-
- Witkop CJ. Hereditary defects of dentin. Dental Clinics of North America. 1975;19(1):25–45. - PubMed
-
- Scola SM, Watts PG. Dentinal dysplasia type I. A subclassification. British Journal of Orthodontics. 1987;14(3):175–179. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources