Ehlers Danlos Syndrome: An Unusual Presentation You Need to Know about
- PMID: 23762718
- PMCID: PMC3670523
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/764659
Ehlers Danlos Syndrome: An Unusual Presentation You Need to Know about
Abstract
The Ehlers Danlos syndromes (EDS) comprise a group of connective tissue disorders characterized by tissue fragility of the skin, ligaments, blood vessels and internal organs. Variable degrees of clinical severity and organ involvement are due to the molecular and biochemical heterogeneity of this group of disorders and have led to classification into well-characterized subtypes that are extending with the discovery of new genes and overlapping syndrome. Types include classical EDS (EDS I/II), hypermobility EDS (EDS III), vascular EDS (EDS IV), kyphoscoliosis EDS (EDS VI), arthrochalasia (EDS VIIA, B) and Dermatospraxis (EDS VIIC). Even to the well trained professional, the diagnosis of EDS remains a challenge due to overlapping symptoms and cases can remain without a well-defined classification. Life altering complications of this group of disorders include vascular and hollow organ rupture and ligamentous laxity leading to chronic dislocation with ensuing pain and long term disability. Patients initially present to the general practitioner who is expected to recognize the symptoms of EDS and to proceed with appropriate referral for definitive diagnosis and management to prevent devastating complications. In this paper, we describe a male with classical EDS complicated by devastating vascular and orthopedic events.
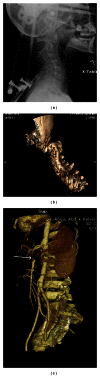
Figures
References
-
- Callewaert B, Malfait F, Loeys B, De Paepe A. Ehlers-Danlos syndromes and Marfan syndrome. Best Practice and Research: Clinical Rheumatology. 2008;22(1):165–189. - PubMed
-
- De Paepe A, Malfait F. The Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, a disorder with many faces. Clinical Genetics. 2012;82(1):1–11. - PubMed
-
- Mories A. Ehlers Danlos Syndrome with a report of a fatal Case. Scottish Medical Journal. 1960;5:269–272. - PubMed
-
- Pepin M, Schwarze U, Superti-Furga A, Byers PH. Clinical and genetic features of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV, the vascular type. New England Journal of Medicine. 2000;342(10):673–680. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

