Moderate-level prenatal alcohol exposure enhances acoustic startle magnitude and disrupts prepulse inhibition in adult rhesus monkeys
- PMID: 23763712
- PMCID: PMC3776014
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.12151
Moderate-level prenatal alcohol exposure enhances acoustic startle magnitude and disrupts prepulse inhibition in adult rhesus monkeys
Abstract
Background: Prenatal alcohol exposure can contribute to a wide range of neurodevelopmental impairments in children and adults including behavioral and neuropsychiatric disorders. In rhesus monkeys, we examined whether moderate-level prenatal alcohol exposure would alter acoustic startle responses and prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle. PPI is a highly quantifiable measure of inhibitory neural processes or sensorimotor gating associated with neuropsychiatric disorders.
Methods: Acoustic startle and PPI of the acoustic startle were tested in 37 adult rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) from 4 experimental conditions: (i) moderate-level prenatal alcohol-exposed, (ii) prenatally stressed, (iii) moderate-level prenatal alcohol-exposed + prenatally stressed, and (iv) sucrose controls.
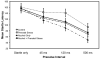
Results: Prenatal alcohol-exposed monkeys showed a higher magnitude of acoustic startle response and disrupted PPI compared with monkeys not exposed to alcohol prenatally. Monkeys in all conditions showed higher hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) axis responses after undergoing the startle procedure, but HPA responses were unrelated to startle response magnitude, latency, or PPI.
Conclusions: Finding altered PPI in monkeys prenatally exposed to a moderate dose of alcohol suggests that reduced sensorimotor gating is 1 effect of prenatal alcohol exposure. Because reduced sensorimotor gating is observed in many neuropsychiatric disorders, sensorimotor gating deficits could be an aspect of the comorbidity between fetal alcohol spectrum disorder and mental health conditions.
Keywords: Acoustic Startle Response; Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder; Inhibitory Control; Mental Health; Prepulse Inhibition.
Copyright © 2013 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures



References
-
- Ayres AJ. Sensory integration and learning disorders. Western Psychological Services; Los Angeles: 1972.
-
- Baer JS, Sampson PD, Barr HM, Connor PD, Streissguth AP. A 21-year longitudinal analysis of the effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on young adult drinking. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60:377–385. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin DS, Montgomery SA, Nil R, Lader M. Discontinuation symptoms in depression and anxiety disorders. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007;10:73–84. - PubMed
-
- Braff DL, Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR. Human studies of prepulse inhibition of startle: normal subjects, patient groups, and pharmacological studies. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2001;156:234–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

