p53-dependent delayed effects of radiation vary according to time of irradiation of p53 + / - mice
- PMID: 23764457
- PMCID: PMC3885116
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrt083
p53-dependent delayed effects of radiation vary according to time of irradiation of p53 + / - mice
Abstract
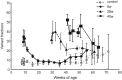
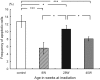
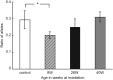
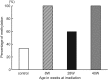
We previously reported that in p53 (+ / -) mice that had been given a whole-body dose of 3 Gy at 8 weeks of age, p53-dependent delayed effects of radiation, as manifested in T-cell receptor (TCR) variant fractions (VF) instability in mouse splenocytes, were biphasic, namely, induction of TCR-VF mutation reappeared at 44 weeks. The manifestation of the delayed effects and the measures of biological markers varied according to the timing of irradiation. We also reported that the decrease in function of the p53 gene was related to the effects of a delayed mutation. In the present study, we investigated the functions and mutations of the p53 gene in old age for p53 (+ / -) mice following irradiation at various ages. p53 (+ / -) mice were given a whole-body dose of 3 Gy at 8, 28 or 40 weeks of age. There were significant differences for all variables tested at 8 weeks of age. This was similarly the case for mice irradiated at 28 weeks of age, in which there were also significant differences in TCR VF and the percentage of apoptosis. In mice irradiated at 40 weeks of age, there were significant differences for all considered variables except for the p53 allele. We demonstrated that the different patterns of delayed mutation of the p53 gene at 56 weeks of age depended on the age at which mice had undergone 3-Gy whole-body irradiation. Our conclusions are limited to variation in p53-dependent delayed effects according to the time of irradiation.
Keywords: age; delayed effects; irradiation; p53.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The delayed manifestation of T-cell receptor (TCR) variants in X-irradiated mice depends on Trp53 status.Radiat Res. 2006 Jul;166(1 Pt 1):55-60. doi: 10.1667/RR3583.1. Radiat Res. 2006. PMID: 16808620
-
Direct detection of p53 -/- thymocyte appearing at an early stage of radiation-induced thymic lymphomagenesis in p53 +/- heterozygous B10 mice.Int J Radiat Biol. 2007 Apr;83(4):259-67. doi: 10.1080/09553000701222780. Int J Radiat Biol. 2007. PMID: 17575953
-
Dynamics of delayed p53 mutations in mice given whole-body irradiation at 8 weeks.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011 Jan 1;79(1):247-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.07.022. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. PMID: 20932652
-
A comprehensive study of p53 transcriptional activity in thymus and spleen of gamma irradiated mouse: high sensitivity of genes involved in the two main apoptotic pathways.Int J Radiat Biol. 2006 Nov;82(11):761-70. doi: 10.1080/09553000600949624. Int J Radiat Biol. 2006. PMID: 17148260
-
[Induction of glutathione and activation of immune functions by low-dose, whole-body irradiation with gamma-rays].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2006 Oct;126(10):849-57. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.126.849. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2006. PMID: 17016016 Review. Japanese.
References
-
- Preston DL, Shimizu Y, Pierce DA, et al. Studies of mortality of atomic bomb survivors. Report 13: Solid cancer and noncancer disease mortality: 1950–1997. Radiat Res. 2003;160:381–407. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki K, Takahara R, Kodama S, et al. In situ detection of chromosome bridge formation and delayed reproductive death in normal human embryonic cells surviving X irradiation. Radiat Res. 1998;150:375–81. - PubMed
-
- Pampfer S, Streffer C. Increased chromosome aberration levels in cells from mouse fetuses after zygote X-irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol. 1989;55:85–92. - PubMed
-
- Barber RC, Hardwick RJ, Shanks ME, et al. The effects of in utero irradiation on mutation induction and transgenerational instability in mice. Mut Res. 2009;664:6–12. - PubMed
-
- Hall EJ. Radiation biology for pediatric radiologists. Pediatr Radiol. 2009;39(Suppl 1):S57–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

