Antibacterial activity of selected commercial products for mouth washing and disinfection, assessed in accordance with PN-EN 1040
- PMID: 23764523
- PMCID: PMC3692377
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.883952
Antibacterial activity of selected commercial products for mouth washing and disinfection, assessed in accordance with PN-EN 1040
Abstract
Background: Currently, there is a wide range of products for mouth washing on the Polish market. They have different qualitative and quantitative compositions, and they differ particularly in the concentration of active substances. In antisepsis and disinfection, the significant reduction in number of cells of microorganisms in a particular environment is very crucial. The chemical agents should provide a significant decrease in number of microorganisms in a relatively short time. The purpose of this study was to examine the bactericidal activity of selected herbal products used for treatment of inflammation, and disinfection and washing of the mouth, having antibacterial activity as declared by the manufacturers.
Material and methods: The study included 28 products for mouth washing and disinfection available in Poland. Bactericidal activity was studied using a quantitative suspension test according to the standard PN-EN 1040.
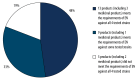
Results: Only 1 of 4 tested herbal products, registered as medicinal products, showed satisfactory antibacterial activity when they were used according to the manufacturer's recommendations. A total of 13 preparations (48%) complied with the standard requirements against all tested strains. Up to 19% of products showed no bactericidal activity against bacterial strains, and up to 33% were only effective against certain microorganisms.
Conclusions: The informational literature accompanying most antiseptics should be corrected by the manufacturers, providing information about antimicrobial activity consistent with the requirements of applicable standards. The information on the packaging or in the leaflets for antiseptic products should be corrected by the manufacturers to include accurate information on antimicrobial activity.
Figures
References
-
-
Standard PN-EN 1040 Chemical disinfectants and antiseptics – Quantitative suspension test for the evaluation of Basic bactericidal activity of chemical disinfectants and antiseptics – Test method and requirements (phase1). Polish Committee for Standardization (PKN) 2000
-
-
-
Standard EN 13727 Chemical disinfectants and antiseptics - Quantitative suspension test for the evaluation of bactericidal activity in medical area – Test method and requirements (phase 2/step 1) CEN 2012
-
-
- Hayes AJ, Leach DN, Markham JL, Markowic B. In vitro cytotoxicity of Australia tea tree oil using human cell lines. Oil Res. 1997;9:575–82.
-
- Shapiro S, Meier A, Guggenheim B. The antimicrobial activity of essential oils and essentials oil components towards oral bacteria. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1994;9:202–8. - PubMed
-
- Adams S, Kunz B. Mycelial deformations of Cladosporium herbarum due to the application of eugenol or carvacrol. J Essen Oil Res. 1996;8:535–45.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials