Deep mutational scanning of an antibody against epidermal growth factor receptor using mammalian cell display and massively parallel pyrosequencing
- PMID: 23765106
- PMCID: PMC3906306
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.24979
Deep mutational scanning of an antibody against epidermal growth factor receptor using mammalian cell display and massively parallel pyrosequencing
Abstract
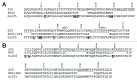
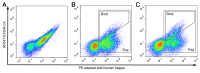
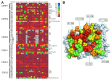
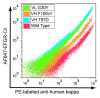
We developed a method for deep mutational scanning of antibody complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) that can determine in parallel the effect of every possible single amino acid CDR substitution on antigen binding. The method uses libraries of full length IgGs containing more than 1000 CDR point mutations displayed on mammalian cells, sorted by flow cytometry into subpopulations based on antigen affinity and analyzed by massively parallel pyrosequencing. Higher, lower and neutral affinity mutations are identified by their enrichment or depletion in the FACS subpopulations. We applied this method to a humanized version of the anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody cetuximab, generated a near comprehensive data set for 1060 point mutations that recapitulates previously determined structural and mutational data for these CDRs and identified 67 point mutations that increase affinity. The large-scale, comprehensive sequence-function data sets generated by this method should have broad utility for engineering properties such as antibody affinity and specificity and may advance theoretical understanding of antibody-antigen recognition.
Keywords: EGFR; antibody engineering; cetuximab; mammalian display; next generation sequencing.
Figures

References
-
- Sato JD, Kawamoto T, Le AD, Mendelsohn J, Polikoff J, Sato GH. Biological effects in vitro of monoclonal antibodies to human epidermal growth factor receptors. Mol Biol Med. 1983;1:511–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
