Myeloablative anti-CD20 radioimmunotherapy +/- high-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell support for relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphoma results in excellent long-term survival
- PMID: 23765188
- PMCID: PMC3757247
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.1037
Myeloablative anti-CD20 radioimmunotherapy +/- high-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell support for relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphoma results in excellent long-term survival
Abstract
Background: Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) has been used to treat relapsed/refractory CD20+ Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Myeloablative anti-CD20 RIT followed by autologous stem cell infusion (ASCT) enables high radiation doses to lymphoma sites. We performed a phase I/II trial to assess feasibility and survival.
Methods: Twenty-three patients with relapsed/refractory NHL without complete remission (CR) to salvage chemotherapy were enrolled to evaluate RIT with Iodine-131 labelled rituximab (131I-rituximab) in a myeloablative setting. Biodistribution and dosimetric studies were performed to determine 131I activity required to induce a total body dose of 21-27Gy to critical organs. In 6/23 patients RIT was combined with high-dose chemotherapy. 8/23 patients received a sequential high-dose chemotherapy with a second ASCT. The median follow-up is 9.5 years.
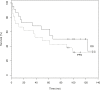
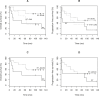
Results: 6.956-19.425GBq of 131I was delivered to achieve the limiting organ dose to lungs or kidneys. No grade III/IV non-hematologic toxicity was seen with RIT alone. Significant grade III/IV toxicity (mucositis, fever, infection, one therapy related death) was observed in patients treated with RIT combined with high-dose chemotherapy. The overall response rate was 87% (64% CR). The median progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS) is 47.5 and 101.5 months. An international prognostic index score >1 was predictive for OS.
Conclusion: Myeloablative RIT with 131I-rituximab followed by ASCT is feasible, well-tolerated and effective in high risk CD20+ NHL. Combination of RIT and high-dose chemotherapy increased toxicity significantly. Long-term results for PFS and OS are encouraging.
Figures
Comment in
-
Tandem myeloablative 131I-rituximab radioimmunotherapy and high-dose chemotherapy in refractory/relapsed non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients.Immunotherapy. 2013 Dec;5(12):1283-6. doi: 10.2217/imt.13.138. Immunotherapy. 2013. PMID: 24283837
References
-
- Swerdlow SHC E, Harris N.L, Jaffe E.S, Pileri S.A, Stein H, Thiele J, Vardiman J.W. (Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer); 2008. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues.
-
- DeNardo SJ, DeNardo GL, O'Grady LF, Macey DJ, Mills SL, Epstein AL, Peng JS, McGahan JP. Treatment of a patient with B cell lymphoma by I-131 LYM-1 monoclonal antibodies. Int J Biol Markers. 1987;2(1):49–53. - PubMed
-
- Parker BA, Vassos AB, Halpern SE, Miller RA, Hupf H, Amox DG, Simoni JL, Starr RJ, Green MR, Royston I. Radioimmunotherapy of human B-cell lymphoma with 90Y-conjugated antiidiotype monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 1990;50(3 Suppl):1022s–1028s. - PubMed
-
- Kaminski MS, Zasadny KR, Francis IR, Milik AW, Ross CW, Moon SD, Crawford SM, Burgess JM, Petry NA, Butchko GM, et al. Radioimmunotherapy of B-cell lymphoma with [131I]anti-B1 (anti-CD20) antibody. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(7):459–465. - PubMed
-
- Kaminski MS, Zasadny KR, Francis IR, Fenner MC, Ross CW, Milik AW, Estes J, Tuck M, Regan D, Fisher S, Glenn SD, Wahl RL. Iodine-131-anti-B1 radioimmunotherapy for B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14(7):1974–1981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

