Registration of histological whole slide images guided by vessel structures
- PMID: 23766932
- PMCID: PMC3678747
- DOI: 10.4103/2153-3539.109868
Registration of histological whole slide images guided by vessel structures
Abstract
Introduction: The registration of histological whole slide images is an important prerequisite for modern histological image analysis. A partial reconstruction of the original volume allows e.g. colocalization analysis of tissue parameters or high-detail reconstructions of anatomical structures in 3D.
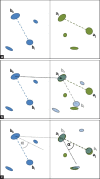
Methods: In this paper, we present an automatic staining-invariant registration method, and as part of that, introduce a novel vessel-based rigid registration algorithm using a custom similarity measure. The method is based on an iterative best-fit matching of prominent vessel structures.
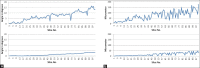
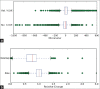
Results: We evaluated our method on a sophisticated synthetic dataset as well as on real histological whole slide images. Based on labeled vessel structures we compared the relative differences for corresponding structures. The average positional error was close to 0, the median for the size change factor was 1, and the median overlap was 0.77.
Conclusion: The results show that our approach is very robust and creates high quality reconstructions. The key element for the resulting quality is our novel rigid registration algorithm.
Keywords: Elastic registration; histology; rigid registration; vessel structure; whole slide images.
Figures




References
-
- Wirtz S, Fischer B, Modersitzki J, Schmitt O. Super-fast elastic registration of histologic images of a whole rat brain for three-dimensional reconstruction. Proc SPIE. 2004;5370:328–34.
-
- Feuerstein M, Heibel H, Gardiazabal J, Navab N, Groher M. Reconstruction of 3-D histology images by simultaneous deformable registration. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2011;14(Pt 2):582–9. - PubMed
-
- Dauguet J, Delzescaux T, Condé F, Mangin JF, Ayache N, Hantraye P, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of stained histological slices and 3D non-linear registration with in-vivo MRI for whole baboon brain. J Neurosci Methods. 2007;164:191–204. - PubMed
-
- Ourselin S, Roche A, Subsol G, Pennec X, Ayache N. Reconstructing a 3D structure from serial histological sections. Image Vis Comput. 2001;19:25–31.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

