A secreted bacterial protease tailors the Staphylococcus aureus virulence repertoire to modulate bone remodeling during osteomyelitis
- PMID: 23768499
- PMCID: PMC3721972
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.05.003
A secreted bacterial protease tailors the Staphylococcus aureus virulence repertoire to modulate bone remodeling during osteomyelitis
Abstract
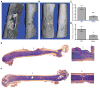
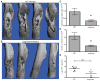
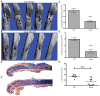
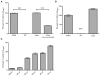
Osteomyelitis is a common manifestation of invasive Staphylococcus aureus infection. Pathogen-induced bone destruction limits antimicrobial penetration to the infectious focus and compromises treatment of osteomyelitis. To investigate mechanisms of S. aureus-induced bone destruction, we developed a murine model of osteomyelitis. Microcomputed tomography of infected femurs revealed that S. aureus triggers profound alterations in bone turnover. The bacterial regulatory locus sae was found to be critical for osteomyelitis pathogenesis, as Sae-regulated factors promote pathologic bone remodeling and intraosseous bacterial survival. Exoproteome analyses revealed the Sae-regulated protease aureolysin as a major determinant of the S. aureus secretome and identified the phenol-soluble modulins as aureolysin-degraded, osteolytic peptides that trigger osteoblast cell death and bone destruction. These studies establish a murine model for pathogen-induced bone remodeling, define Sae as critical for osteomyelitis pathogenesis, and identify protease-dependent exoproteome remodeling as a major determinant of the staphylococcal virulence repertoire.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis: bad to the bone.Cell Host Microbe. 2013 Jun 12;13(6):629-31. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.05.015. Cell Host Microbe. 2013. PMID: 23768487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arvidson S. Studies on extracellular proteolytic enzymes from Staphylococcus aureus. II. Isolation and characterization of an EDTA-sensitive protease. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 1973;302:149–157. - PubMed
-
- Belthur MV, Birchansky SB, Verdugo AA, Mason EO, Jr, Hulten KG, Kaplan SL, Smith EO, Phillips WA, Weinberg J. Pathologic fractures in children with acute Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. The Journal of bone and joint surgery American volume. 2012;94:34–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI091856/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI091856/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD060554/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI074935/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10RR027631-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI073843/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103625/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI069233/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027631/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI069233/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32HD060554-03/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- AI073843/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- L40 AI096516/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

