Selenoprotein P regulates 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-benzo-2,5-quinone-induced oxidative stress and toxicity in human keratinocytes
- PMID: 23770201
- PMCID: PMC3830697
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.06.010
Selenoprotein P regulates 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-benzo-2,5-quinone-induced oxidative stress and toxicity in human keratinocytes
Abstract
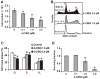
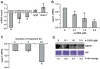
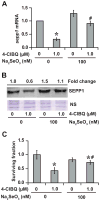
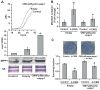
Polychlorinated biphenyls and their metabolites are environmental pollutants that are believed to have adverse health effects presumably by inducing oxidative stress. To determine if 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-benzo-2,5-quinone (4-ClBQ; metabolite of 4-monochlorobiphenyl, PCB3)-induced oxidative stress is associated with changes in the expression of specific antioxidant genes, mRNA levels of 92 oxidative stress-response genes were analyzed using TaqMan Array Human Antioxidant Mechanisms (Life Technologies), and results were verified by performing quantitative RT-PCR assays. The expression of selenoprotein P (sepp1) was significantly downregulated (8- to 10-fold) in 4-ClBQ-treated HaCaT human skin keratinocytes, which correlated with a significant increase in MitoSOX oxidation. Overexpression of Mn-superoxide dismutase or catalase or treatment with N-acetyl-l-cysteine suppressed 4-ClBQ-induced toxicity. Sodium selenite supplementation also suppressed 4-ClBQ-induced decrease in sepp1 expression, which was associated with a significant inhibition in cell death. Furthermore, HaCaT cells overexpressing sepp1 were resistant to 4-ClBQ-induced oxidative stress and toxicity. These results demonstrate that SEPP1 represents a previously unrecognized regulator of PCB-induced biological effects. These results support the speculation that selenoproteins can be an attractive countermeasure for PCB-induced adverse biological effects.
Keywords: 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-benzo-2,5-quinone; 4-ClBQ; 4-monochlorobiphenyl; AdCAT; AdEmpty; AdMnSOD; Free radicals; HaCaT; MFI; N-acetyl-L-cysteine; NAC; Oxidative stress; PCB3; PEG-CAT; PEG-SOD; Polychlorinated biphenyls; ROS; SECIS; SEPP1; Selenoprotein P; adenovirus carrying a control vector without an insert; adenovirus carrying a human Mn-superoxide dismutase cDNA; adenovirus carrying a human catalase cDNA; mean fluorescence intensity; polyethylene glycol–catalase; polyethylene glycol–superoxide dismutase; reactive oxygen species; selenocysteine insertion sequence; selenoprotein P.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no actual or potential competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Polychlorinated biphenyls: human health aspects. Concise International Chemical Assessment Document. 2003;55:1–57.
-
- Hansen LG, DeCaprio AP, Nisbet ICT. PCB congener comparisons reveal exposure histories for residents of Anniston, Alabama, USA. Fresenius Environ Bull. 2003;12:181–190.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

