Na/Ca exchange and contraction of the heart
- PMID: 23770352
- PMCID: PMC3730535
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.06.001
Na/Ca exchange and contraction of the heart
Abstract
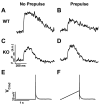
Sodium-calcium exchange (NCX) is the major calcium (Ca) efflux mechanism of ventricular cardiomyocytes. Consequently the exchanger plays a critical role in the regulation of cellular Ca content and hence contractility. Reductions in Ca efflux by the exchanger, such as those produced by elevated intracellular sodium (Na) in response to cardiac glycosides, raise sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca stores. The result is an increased Ca transient and cardiac contractility. Enhanced Ca efflux activity by the exchanger, for example during heart failure, may reduce diadic cleft Ca and excitation-contraction (EC) coupling gain. This aggravates the impaired contractility associated with SR Ca ATPase dysfunction and reduced SR Ca load in failing heart muscle. Recent data from our laboratories indicate that NCX can also impact the efficiency of EC coupling and contractility independent of SR Ca load through diadic cleft priming with Ca during the upstroke of the action potential. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled "Na(+) Regulation in Cardiac Myocytes".
Keywords: AP; Ca; Calcium; EC; Excitation contraction coupling; Genetically modified mice; Heart contractility; Heart failure; KO; L-type Ca channels; LCCs; NCX; NCX knockout mouse; RyRs; SR; Sodium calcium exchanger; action potential; calcium; excitation–contraction coupling; ryanodine receptor; sarcoplasmic reticulum; sodium calcium exchanger.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Liao J, Li H, Zeng W, Sauer DB, Belmares R, Jiang Y. Structural insight into the ion-exchange mechanism of the sodium/calcium exchanger. Science. 2012;335:686–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

