Genome-wide association study identifies multiple risk loci for chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 23770605
- PMCID: PMC3729927
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2652
Genome-wide association study identifies multiple risk loci for chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
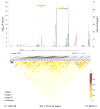
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have previously identified 13 loci associated with risk of chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL). To identify additional CLL susceptibility loci, we conducted the largest meta-analysis for CLL thus far, including four GWAS with a total of 3,100 individuals with CLL (cases) and 7,667 controls. In the meta-analysis, we identified ten independent associated SNPs in nine new loci at 10q23.31 (ACTA2 or FAS (ACTA2/FAS), P=1.22×10(-14)), 18q21.33 (BCL2, P=7.76×10(-11)), 11p15.5 (C11orf21, P=2.15×10(-10)), 4q25 (LEF1, P=4.24×10(-10)), 2q33.1 (CASP10 or CASP8 (CASP10/CASP8), P=2.50×10(-9)), 9p21.3 (CDKN2B-AS1, P=1.27×10(-8)), 18q21.32 (PMAIP1, P=2.51×10(-8)), 15q15.1 (BMF, P=2.71×10(-10)) and 2p22.2 (QPCT, P=1.68×10(-8)), as well as an independent signal at an established locus (2q13, ACOXL, P=2.08×10(-18)). We also found evidence for two additional promising loci below genome-wide significance at 8q22.3 (ODF1, P=5.40×10(-8)) and 5p15.33 (TERT, P=1.92×10(-7)). Although further studies are required, the proximity of several of these loci to genes involved in apoptosis suggests a plausible underlying biological mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests
Figures









References
-
- Di Bernardo MC, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies six susceptibility loci for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nature genetics. 2008;40:1204–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 HG007416/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA148690/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA150037/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154643/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA134919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA104682/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092153/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA134674/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA143947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES004705/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129539/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA098566/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 RC037004/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA097274/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN045165/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA149445/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA118444/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA042014/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

