Immunoglobulin G1 and immunoglobulin G4 antibodies in multiple sclerosis patients treated with IFNβ interact with the endogenous cytokine and activate complement
- PMID: 23770627
- PMCID: PMC3779799
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2013.05.008
Immunoglobulin G1 and immunoglobulin G4 antibodies in multiple sclerosis patients treated with IFNβ interact with the endogenous cytokine and activate complement
Abstract
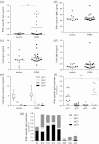
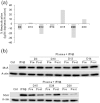
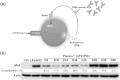
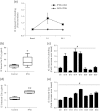
A subset of patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) on therapy with interferon beta (IFNβ) develop neutralising anti-drug antibodies (ADA) resulting in reduced, or loss of, therapeutic efficacy. The aims were to characterise the relative contributions of anti-IFNβ antibody isotypes to drug neutralising activity, ability of these antibodies to cross-react with endogenous IFNβ, to form immune complexes and activate complement. IFNβ-specific ADA were measured in plasma from RRMS patients treated with IFNβ1a (Rebif(®)). Neutralisation of endogenous and therapeutic IFNβ by ADA was determined by IFNβ bioassay. IFNβ-ADA profile was predominantly comprised of IgG1 and IgG4 antibody isotypes. The contribution of IgG4-ADA towards neutralising activity was found to be minimal. Neutralising IFNβ-ADA blocks endogenous IFNβ activity. ADA interaction with therapeutic IFNβ results in immune complex formation and complement activation. In summary, IgG1 and IgG4 IFNβ-ADA have the ability to neutralise therapeutic and endogenous protein and to activate complement.
Keywords: Anti-drug antibody;; Complement; Immunogenicity;; Interferon beta;; Neutralising antibody;; Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis;.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Compston A., Coles A. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 2008;372:1502–1517. - PubMed
-
- Li D.K., Paty D.W. Magnetic resonance imaging results of the PRISMS trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of interferon-beta1a in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Prevention of Relapses and Disability by Interferon-beta1a Subcutaneously in Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 1999;46:197–206. - PubMed
-
- Paty D.W., Li D.K. Interferon beta-1b is effective in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. II. MRI analysis results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. UBC MS/MRI Study Group and the IFNB Multiple Sclerosis Study Group. Neurology. 1993;43:662–667. - PubMed
-
- Perini P., Calabrese M., Biasi G., Gallo P. The clinical impact of interferon beta antibodies in relapsing-remitting MS. J. Neurol. 2004;251:305–309. - PubMed
-
- Sorensen P.S., Koch-Henriksen N., Ross C., Clemmesen K.M., Bendtzen K. Appearance and disappearance of neutralizing antibodies during interferon-beta therapy. Neurology. 2005;65:33–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

