Topological insulator bismuth selenide as a theranostic platform for simultaneous cancer imaging and therapy
- PMID: 23770650
- PMCID: PMC3683666
- DOI: 10.1038/srep01998
Topological insulator bismuth selenide as a theranostic platform for simultaneous cancer imaging and therapy
Abstract
Employing theranostic nanoparticles, which combine both therapeutic and diagnostic capabilities in one dose, has promise to propel the biomedical field toward personalized medicine. Here we investigate the theranostic properties of topological insulator bismuth selenide (Bi2Se3) in in vivo and in vitro system for the first time. We show that Bi2Se3 nanoplates can absorb near-infrared (NIR) laser light and effectively convert laser energy into heat. Such photothermal conversion property may be due to the unique physical properties of topological insulators. Furthermore, localized and irreversible photothermal ablation of tumors in the mouse model is successfully achieved by using Bi2Se3 nanoplates and NIR laser irradiation. In addition, we also demonstrate that Bi2Se3 nanoplates exhibit strong X-ray attenuation and can be utilized for enhanced X-ray computed tomography imaging of tumor tissue in vivo. This study highlights Bi2Se3 nanoplates could serve as a promising platform for cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Figures


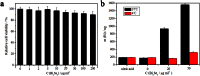
 ) or Iopamidol (
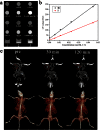
) or Iopamidol ( ) as function of the concentration. (c) CT coronal views of a mouse following an intratumoral injection of 100 μl of Bi2Se3 nanoplates solution (0.2 mol Bi l−1) (top). The corresponding 3D rendering of in vivo CT images above (bottom). The position of tumor is marked by red circles.
) as function of the concentration. (c) CT coronal views of a mouse following an intratumoral injection of 100 μl of Bi2Se3 nanoplates solution (0.2 mol Bi l−1) (top). The corresponding 3D rendering of in vivo CT images above (bottom). The position of tumor is marked by red circles.
References
-
- Cancer [homepage on the Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization. Accessed January 15, 2013. Available from: http://www.who.int/cancer/about/facts/en/.
-
- Funkhouser J. Reinventing pharma: the theranostic revolution. Curr. Drug Discovery 2, 17–19 (2002).
-
- Davis M. E., Chen Z. G. & Shin D. M. Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 7, 771–782 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Petros R. A. & DeSimone J. M. Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 9, 615–627 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

