Danthron activates AMP-activated protein kinase and regulates lipid and glucose metabolism in vitro
- PMID: 23770982
- PMCID: PMC4003022
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2013.39
Danthron activates AMP-activated protein kinase and regulates lipid and glucose metabolism in vitro
Abstract
Aim: To discover the active compound on AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation and investigate the effects of the active compound 1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone (danthron) from the traditional Chinese medicine rhubarb on AMPK-mediated lipid and glucose metabolism in vitro.
Methods: HepG2 and C2C12 cells were used. Cell viability was determined using MTT assay. Real-time PCR was performed to measure the gene expression. Western blotting assay was applied to investigate the protein phosphorylation level. Enzymatic assay kits were used to detect the total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG) and glucose contents.
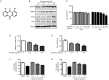
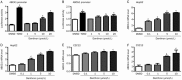
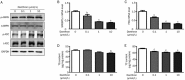
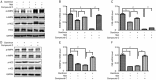
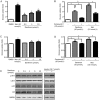
Results: Danthron (0.1, 1, and 10 μmol/L) dose-dependently promoted the phosphorylation of AMPK and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) in both HepG2 and C2C12 cells. Meanwhile, danthron treatment significantly reduced the lipid synthesis related sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP1c) and fatty acid synthetase (FAS) gene expressions, and the TC and TG levels. In addition, danthron treatment efficiently increased glucose consumption. The actions of danthron on lipid and glucose metabolism were abolished or reversed by co-treatment with the AMPK inhibitor compound C.
Conclusion: Danthron effectively reduces intracellular lipid contents and enhanced glucose consumption in vitro via activation of AMPK signaling pathway.
Figures
References
-
- DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E. Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care. 1991;14:173–94. - PubMed
-
- Grundy SM. Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:2595–600. - PubMed
-
- Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D, Hardie DG. AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 2005;1:15–25. - PubMed
-
- Zhang BB, Zhou G, Li C. AMPK: an emerging drug target for diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab. 2009;9:407–16. - PubMed
-
- Yu LF, Qiu BY, Nan FJ, Li J. AMPK activators as novel therapeutics for type 2 diabetes. Curr Top Med Chem. 2010;10:397–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

