Parkinson disease affects peripheral sensory nerves in the pharynx
- PMID: 23771215
- PMCID: PMC3695629
- DOI: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3182965886
Parkinson disease affects peripheral sensory nerves in the pharynx
Abstract
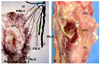
Dysphagia is very common in patients with Parkinson disease (PD) and often leads to aspiration pneumonia, the most common cause of death in PD. Current therapies are largely ineffective for dysphagia. Because pharyngeal sensation normally triggers the swallowing reflex, we examined pharyngeal sensory nerves in PD patients for Lewy pathology.Sensory nerves supplying the pharynx were excised from autopsied pharynges obtained from patients with clinically diagnosed and neuropathologically confirmed PD (n = 10) and healthy age-matched controls (n = 4). We examined the glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve IX), the pharyngeal sensory branch of the vagus nerve (PSB-X), and the internal superior laryngeal nerve (ISLN) innervating the laryngopharynx. Immunohistochemistry for phosphorylated α-synuclein was used to detect Lewy pathology. Axonal α-synuclein aggregates in the pharyngeal sensory nerves were identified in all of the PD subjects but not in the controls. The density of α-synuclein-positive lesions was greater in PD patients with dysphagia versus those without dysphagia. In addition, α-synuclein-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the ISLN were much more abundant than those in cranial nerve IX and PSB-X. These findings suggest that pharyngeal sensory nerves are directly affected by pathologic processes in PD. These abnormalities may decrease pharyngeal sensation, thereby impairing swallowing and airway protective reflexes and contributing to dysphagia and aspiration.
Figures

References
-
- Jankovic J. Parkinson’s disease: clinical features and diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79:368–376. - PubMed
-
- Ramig LO, Fox C, Sapir S. Speech Treatment for Parkinson’s disease. Expert Rev Neurother. 2008;8:297–309. - PubMed
-
- Sapir S, Ramig L, Fox C. Speech and swallowing disorders in Parkinson disease. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;16:205–210. - PubMed
-
- Duff J, Sime E. Surgical interventions in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD) and essential tremor (ET): medial pallidotomy in PD and chronic deep brain stimulation (DBS) in PD and ET. Axon. 1997;18:85–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

