Fork sensing and strand switching control antagonistic activities of RecQ helicases
- PMID: 23771268
- PMCID: PMC3709500
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms3024
Fork sensing and strand switching control antagonistic activities of RecQ helicases
Abstract
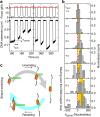
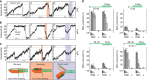
RecQ helicases have essential roles in maintaining genome stability during replication and in controlling double-strand break repair by homologous recombination. Little is known about how the different RecQ helicases found in higher eukaryotes achieve their specialized and partially opposing functions. Here, we investigate the DNA unwinding of RecQ helicases from Arabidopsis thaliana, AtRECQ2 and AtRECQ3 at the single-molecule level using magnetic tweezers. Although AtRECQ2 predominantly unwinds forked DNA substrates in a highly repetitive fashion, AtRECQ3 prefers to rewind, that is, to close preopened DNA forks. For both enzymes, this process is controlled by frequent strand switches and active sensing of the unwinding fork. The relative extent of the strand switches towards unwinding or towards rewinding determines the predominant direction of the enzyme. Our results provide a simple explanation for how different biological activities can be achieved by rather similar members of the RecQ family.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Biochemical characterization of AtRECQ3 reveals significant differences relative to other RecQ helicases.Plant Physiol. 2009 Nov;151(3):1658-66. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.144709. Epub 2009 Sep 15. Plant Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19755539 Free PMC article.
-
AtRECQ2, a RecQ helicase homologue from Arabidopsis thaliana, is able to disrupt various recombinogenic DNA structures in vitro.Plant J. 2008 Aug;55(3):397-405. doi: 10.1111/j.0960-7412.2008.03511.x. Plant J. 2008. PMID: 18419780
-
The RecQ-like helicase HRQ1 is involved in DNA crosslink repair in Arabidopsis in a common pathway with the Fanconi anemia-associated nuclease FAN1 and the postreplicative repair ATPase RAD5A.New Phytol. 2018 Jun;218(4):1478-1490. doi: 10.1111/nph.15109. Epub 2018 Mar 25. New Phytol. 2018. PMID: 29577315
-
RecQ helicases in DNA double strand break repair and telomere maintenance.Mutat Res. 2012 Aug 1;736(1-2):15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.06.002. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Mutat Res. 2012. PMID: 21689668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RecQ Family Helicases in Replication Fork Remodeling and Repair: Opening New Avenues towards the Identification of Potential Targets for Cancer Chemotherapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020;20(11):1311-1326. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200518082433. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32418530 Review.
Cited by
-
Branched unwinding mechanism of the Pif1 family of DNA helicases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Dec 3;116(49):24533-24541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1915654116. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31744872 Free PMC article.
-
Single molecule kinetics uncover roles for E. coli RecQ DNA helicase domains and interaction with SSB.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Sep 19;46(16):8500-8515. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky647. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30053104 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic look at DNA unwinding by a replicative helicase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Mar 4;111(9):E827-35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1322254111. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24550505 Free PMC article.
-
A mechanistic study of helicases with magnetic traps.Protein Sci. 2017 Jul;26(7):1314-1336. doi: 10.1002/pro.3187. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Protein Sci. 2017. PMID: 28474797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The HRDC domain oppositely modulates the unwinding activity of E. coli RecQ helicase on duplex DNA and G-quadruplex.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 18;295(51):17646-17658. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015492. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33454004 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

