Conditional deletion of FAK in mice endothelium disrupts lung vascular barrier function due to destabilization of RhoA and Rac1 activities
- PMID: 23771883
- PMCID: PMC3891015
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00094.2013
Conditional deletion of FAK in mice endothelium disrupts lung vascular barrier function due to destabilization of RhoA and Rac1 activities
Abstract
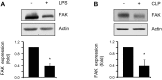
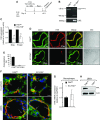
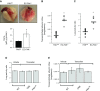
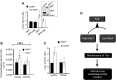
Loss of lung-fluid homeostasis is the hallmark of acute lung injury (ALI). Association of catenins and actin cytoskeleton with vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin is generally considered the main mechanism for stabilizing adherens junctions (AJs), thereby preventing disruption of lung vascular barrier function. The present study identifies endothelial focal adhesion kinase (FAK), a nonreceptor tyrosine kinase that canonically regulates focal adhesion turnover, as a novel AJ-stabilizing mechanism. In wild-type mice, induction of ALI by intraperitoneal administration of lipopolysaccharide or cecal ligation and puncture markedly decreased FAK expression in lungs. Using a mouse model in which FAK was conditionally deleted only in endothelial cells (ECs), we show that loss of EC-FAK mimicked key features of ALI (diffuse lung hemorrhage, increased transvascular albumin influx, edema, and neutrophil accumulation in the lung). EC-FAK deletion disrupted AJs due to impairment of the fine balance between the activities of RhoA and Rac1 GTPases. Deletion of EC-FAK facilitated RhoA's interaction with p115-RhoA guanine exchange factor, leading to activation of RhoA. Activated RhoA antagonized Rac1 activity, destabilizing AJs. Inhibition of Rho kinase, a downstream effector of RhoA, reinstated normal endothelial barrier function in FAK-/- ECs and lung vascular integrity in EC-FAK-/- mice. Our findings demonstrate that EC-FAK plays an essential role in maintaining AJs and thereby lung vascular barrier function by establishing the normal balance between RhoA and Rac1 activities.
Keywords: acute lung injury; adherens junctions; endothelial barrier; focal adhesion kinase.
Figures


References
-
- Bachmaier K, Toya S, Gao X, Triantafillou T, Garrean S, Park GY, Frey RS, Vogel S, Minshall R, Christman JW, Tiruppathi C, Malik AB. E3 ubiquitin ligase Cblb regulates the acute inflammatory response underlying lung injury. Nat Med 13: 920–926, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Carbajal JM, Schaeffer RC., Jr RhoA inactivation enhances endothelial barrier function. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 277: C955–C964, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

