Visual predictions in the orbitofrontal cortex rely on associative content
- PMID: 23771980
- PMCID: PMC4193460
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bht146
Visual predictions in the orbitofrontal cortex rely on associative content
Abstract
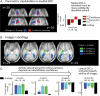
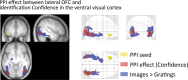
Predicting upcoming events from incomplete information is an essential brain function. The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) plays a critical role in this process by facilitating recognition of sensory inputs via predictive feedback to sensory cortices. In the visual domain, the OFC is engaged by low spatial frequency (LSF) and magnocellular-biased inputs, but beyond this, we know little about the information content required to activate it. Is the OFC automatically engaged to analyze any LSF information for meaning? Or is it engaged only when LSF information matches preexisting memory associations? We tested these hypotheses and show that only LSF information that could be linked to memory associations engages the OFC. Specifically, LSF stimuli activated the OFC in 2 distinct medial and lateral regions only if they resembled known visual objects. More identifiable objects increased activity in the medial OFC, known for its function in affective responses. Furthermore, these objects also increased the connectivity of the lateral OFC with the ventral visual cortex, a crucial region for object identification. At the interface between sensory, memory, and affective processing, the OFC thus appears to be attuned to the associative content of visual information and to play a central role in visuo-affective prediction.
Keywords: fMRI; perception; top-down.
© The Author 2013. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Andrade A, Paradis AL, Rouquette S, Poline JB. Ambiguous results in functional neuroimaging data analysis due to covariate correlation. NeuroImage. 1999;10:483–486. - PubMed
-
- Bachevalier J, Mishkin M. Visual recognition impairment follows ventromedial but not dorsolateral prefrontal lesions in monkeys. Behav Brain Res. 1986;20:249–261. - PubMed
-
- Bar M. Visual objects in context. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:617–629. - PubMed
-
- Bar M, Tootell RBH, Schacter DL, Greve DN, Fischl B, Mendola JD, Rosen BR, Dale AM. Cortical mechanisms specific to explicit visual object recognition. Neuron. 2001;29:529–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

