Clostridium scindens: a human gut microbe with a high potential to convert glucocorticoids into androgens
- PMID: 23772041
- PMCID: PMC3735941
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M038869
Clostridium scindens: a human gut microbe with a high potential to convert glucocorticoids into androgens
Abstract
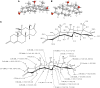
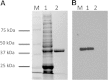
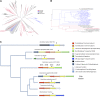
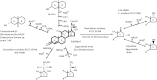
Clostridium scindens American Type Culture Collection 35704 is capable of converting primary bile acids to toxic secondary bile acids, as well as converting glucocorticoids to androgens by side-chain cleavage. The molecular structure of the side-chain cleavage product of cortisol produced by C. scindens was determined to be 11β-hydroxyandrost-4-ene-3,17-dione (11β-OHA) by high-resolution mass spectrometry, (1)H and (13)C NMR spectroscopy, and X-ray crystallography. Using RNA-Seq technology, we identified a cortisol-inducible (≈ 1,000-fold) operon (desABCD) encoding at least one enzyme involved in anaerobic side-chain cleavage. The desC gene was cloned, overexpressed, purified, and found to encode a 20α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSDH). This operon also encodes a putative "transketolase" (desAB) hypothesized to have steroid-17,20-desmolase/oxidase activity, and a possible corticosteroid transporter (desD). RNA-Seq data suggests that the two-carbon side chain of glucocorticords may feed into the pentose-phosphate pathway and are used as a carbon source. The 20α-HSDH is hypothesized to function as a metabolic "rheostat" controlling rates of side-chain cleavage. Phylogenetic analysis suggests this operon is rare in nature and the desC gene evolved from a gene encoding threonine dehydrogenase. The physiological effect of 11β-OHAD on the host or other gut microbes is currently unknown.
Keywords: RNA-Seq; microbiome; steroid.
Figures



References
-
- Ridlon J. M., Kang D. J., Hylemon P. B. 2006. Bile salt biotransformations by human intestinal bacteria. J. Lipid Res. 47: 241–259. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald I. A., Bokkenheuser V. D., Winter J., McLernon A. M., Mosbach E. H. 1983. Degradation of steroids in the human gut. J. Lipid Res. 24: 675–700. - PubMed
-
- Vlahcevic Z. R., Heuman D. M., Hylemon P. B. 1996. Physiology and pathophysiology of enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. In Hepatology: A Textbook of Liver Disease. 3rd edition. Vol. 1. D. Zakim and T. Boyer, editors. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA. 376–417.
-
- Berr F., Kullak-Ublick G. A., Paumgartner G., Munzig W., Hylemon P. B. 1996. 7 alpha-dehydroxylating bacteria enhance deoxycholic acid input and cholesterol saturation of bile in patients with gallstones. Gastroenterology. 111: 1611–1620. - PubMed
-
- Morris G. N., Winter J., Cato E. P., Ritchie A. E., Bokkenheuser V. D. 1985. Clostridium scindens sp. nov., a human intestinal bacterium with desmolytic activity on corticoids. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 35: 478–481.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

