Crippling the essential GTPase Der causes dependence on ribosomal protein L9
- PMID: 23772068
- PMCID: PMC3754568
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00464-13
Crippling the essential GTPase Der causes dependence on ribosomal protein L9
Abstract
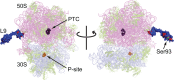
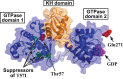
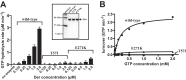
Ribosomal protein L9 is a component of all eubacterial ribosomes, yet deletion strains display only subtle growth defects. Although L9 has been implicated in helping ribosomes maintain translation reading frame and in regulating translation bypass, no portion of the ribosome-bound protein seems capable of contacting either the peptidyltransferase center or the decoding center, so it is a mystery how L9 can influence these important processes. To reveal the physiological roles of L9 that have maintained it in evolution, we identified mutants of Escherichia coli that depend on L9 for fitness. In this report, we describe a class of L9-dependent mutants in the ribosome biogenesis GTPase Der (EngA/YphC). Purified mutant proteins were severely compromised in their GTPase activities, despite the fact that the mutations are not present in GTP hydrolysis sites. Moreover, although L9 and YihI complemented the slow-growth der phenotypes, neither factor could rescue the GTPase activities in vitro. Complementation studies revealed that the N-terminal domain of L9 is necessary and sufficient to improve the fitness of these Der mutants, suggesting that this domain may help stabilize compromised ribosomes that accumulate when Der is defective. Finally, we employed a targeted degradation system to rapidly deplete L9 from a highly compromised der mutant strain and show that the L9-dependent phenotype coincides with a cell division defect.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heterologous Expression of Der Homologs in an Escherichia coli der Mutant and Their Functional Complementation.J Bacteriol. 2016 Aug 11;198(17):2284-96. doi: 10.1128/JB.00384-16. Print 2016 Sep 1. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27297882 Free PMC article.
-
The tandem GTPase, Der, is essential for the biogenesis of 50S ribosomal subunits in Escherichia coli.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Sep;61(6):1660-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05348.x. Epub 2006 Aug 23. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16930151
-
Era and RbfA have overlapping function in ribosome biogenesis in Escherichia coli.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006;11(1-2):41-52. doi: 10.1159/000092818. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16825789
-
A bacterial GAP-like protein, YihI, regulating the GTPase of Der, an essential GTP-binding protein in Escherichia coli.J Mol Biol. 2010 Jun 25;399(5):759-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.04.040. Epub 2010 Apr 29. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20434458
-
Assembly of bacterial ribosomes.Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80:501-26. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-062608-160432. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21529161 Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering a delicate balance between endonuclease RNase III and ribosomal protein S15 in E. coli ribosome assembly.Biochimie. 2021 Dec;191:104-117. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2021.09.003. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Biochimie. 2021. PMID: 34508826 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous Expression of Der Homologs in an Escherichia coli der Mutant and Their Functional Complementation.J Bacteriol. 2016 Aug 11;198(17):2284-96. doi: 10.1128/JB.00384-16. Print 2016 Sep 1. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27297882 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the function of a unique tandem GTPase EngA in bacterial ribosome assembly.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Dec 1;42(21):13430-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1135. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25389271 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Importance of Mobile Ribosomal Proteins.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:539238. doi: 10.1155/2015/539238. Epub 2015 Sep 20. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26457300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The large ribosomal subunit protein L9 enables the growth of EF-P deficient cells and enhances small subunit maturation.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 16;10(4):e0120060. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120060. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25879934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson DN, Nierhaus KH. 2005. Ribosomal proteins in the spotlight. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 40:243–267 - PubMed
-
- Häuser R, Pech M, Kijek J, Yamamoto H, Titz B, Naeve F, Tovchigrechko A, Yamamoto K, Szaflarski W, Takeuchi N, Stellberger T, Diefenbacher ME, Nierhaus KH, Uetz P. 2012. RsfA (YbeB) proteins are conserved ribosomal silencing factors. PLoS Genet. 8:e1002815.10.1371/journal.pgen.1002815 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huber D, Rajagopalan N, Preissler S, Rocco MA, Merz F, Kramer G, Bukau B. 2011. SecA interacts with ribosomes in order to facilitate posttranslational translocation in bacteria. Mol. Cell 41:343–353 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

