Toxic inhalational injury-associated interstitial lung disease in children
- PMID: 23772158
- PMCID: PMC3678010
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.6.915
Toxic inhalational injury-associated interstitial lung disease in children
Abstract
Interstitial lung disease in children (chILD) is a group of disorders characterized by lung inflammation and interstitial fibrosis. In the past recent years, we noted an outbreak of child in Korea, which is possibly associated with inhalation toxicity. Here, we report a series of cases involving toxic inhalational injury-associated chILD with bronchiolitis obliterans pattern in Korean children. This study included 16 pediatric patients confirmed by lung biopsy and chest computed tomography, between February 2006 and May 2011 at Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital. The most common presenting symptoms were cough and dyspnea. The median age at presentation was 26 months (range: 12-47 months), with high mortality (44%). Histopathological analysis showed bronchiolar destruction and centrilobular distribution of alveolar destruction by inflammatory and fibroproliferative process with subpleural sparing. Chest computed tomography showed ground-glass opacities and consolidation in the early phase and diffuse centrilobular nodular opacity in the late phase. Air leak with severe respiratory difficulty was associated with poor prognosis. Although respiratory chemicals such as humidifier disinfectants were strongly considered as a cause of this disease, further studies are needed to understand the etiology and pathophysiology of the disease to improve the prognosis and allow early diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: Bronchioles; Inhalation; Lung Disease, Interstitial; Pulmonary Fibrosis; Toxin, Biological.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial arrangement to disclose.
Figures
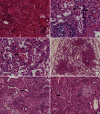
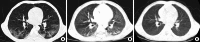
References
-
- Deschildre A, Leclerc F, Hue V, Martinot A, Flurin V, Fourier C, Devisme L, Ramon P, Wallaert B. Treatment with intermittent high dosage corticotherapy in chronic interstitial pneumonia in an infant: a case report. Rev Mal Respir. 1994;11:509–512. - PubMed
-
- Clement A, Eber E. Interstitial lung diseases in infants and children. Eur Respir J. 2008;31:658–666. - PubMed
-
- Cheon CK, Jin HS, Kang EK, Kim HB, Kim BJ, Yu J, Park SJ, Hong SJ, Park JD. Epidemic acute interstitial pneumonia in children occurred during the early 2006s. Korean J Pediatr. 2008;51:383–390.
-
- Kim BJ, Kim HA, Song YH, Yu J, Kim S, Park SJ, Kim KW, Kim KE, Kim DS, Park JD, et al. Nationwide surveillance of acute interstitial pneumonia in Korea. Korean J Pediatr. 2009;52:324–329.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

