2-[2-[4-[2-[2-[ 1,3-Dihydro- 1,1-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-oxo-5-isobenzofuranthioureidyl]ethylaminocarbonyl]ethyl]phenyl] ethylamino]-5'- N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (FITC-APEC): A Fluorescent Ligand For A2a-Adenosine Receptors
- PMID: 23772170
- PMCID: PMC3682427
- DOI: 10.1007/BF00865279
2-[2-[4-[2-[2-[ 1,3-Dihydro- 1,1-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-oxo-5-isobenzofuranthioureidyl]ethylaminocarbonyl]ethyl]phenyl] ethylamino]-5'- N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (FITC-APEC): A Fluorescent Ligand For A2a-Adenosine Receptors
Abstract
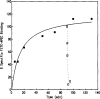
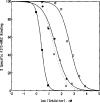
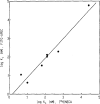
The fluorescein conjugate, FITC-APEC (2-[2-[4-[2-[2-[1,3-dihydro-l,l-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-oxo-5-isobenzofuranthioureidyl]ethylaminocarbonyl]ethyl]phenyl]ethylamino]-5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine), is a novel ligand derived from a series of functionalized congeners that act as selective A2a-adenosine receptor agonists. The binding of FITC-APEC to bovine striatal A2a,-adenosine receptors measured by fluorescence techniques was saturable and of a high affinity, with a Bmax, of 2.3 ± 0.3 pmol/mg protein and KD of 57 ± 2 nM. The KD value estimated by fluorescence was consistent with the Ki (11 ± 0.3 nM) obtained by competition studies with [3H]CGS 21680. Additionally, the Bmax, value found by FITC-APEC measurement was in agreement with Bmax, values obtained using radioligand binding. FITC-APEC exhibited rapid and reversible binding to bovine striatum. The potencies of chemically diverse A2a-adenosine receptor ligands estimated by inhibition of FITC-APEC binding were in good agreement with their potencies determined using radioligand binding techniques (r = 0.97, P = 0.0003). FITC-APEC binding was not altered by purine derivatives that do not recognize A2a-adenosine receptors. These findings demonstrate that the novel fluorescent ligand FITC-APEC can be used in the quantitative characterization of ligand binding to A2a-adenosine receptors.
Keywords: A2a-adenosine receptors; Fluorescence; bovine striatum; receptor binding.
Figures
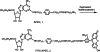

References
-
- Yamamura HI, Enna SJ, Kuhar MJ. Neuro-transmitter Receptor Binding. Raven Press; New York: 1983.
-
- Snyder SH. JAMA. 1989;261:3126–3129. - PubMed
-
- McCabe RT, de Costa BR, Miller RL, Havunjian RH, Rice KC, Skolnick P. FASEB J. 1990;4:2934–2940. - PubMed
-
- Havunjian RH, de Costa BR, Rice KC, Skolnick P. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:22181–22186. - PubMed
-
- McCabe RT, Newman AH, Skolnick P. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1992;262:734–740. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
