Solutions for Determining the Significance Region Using the Johnson-Neyman Type Procedure in Generalized Linear (Mixed) Models
- PMID: 23772174
- PMCID: PMC3682820
- DOI: 10.3102/1076998610396889
Solutions for Determining the Significance Region Using the Johnson-Neyman Type Procedure in Generalized Linear (Mixed) Models
Abstract
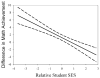
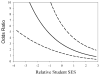
Researchers often compare the relationship between an outcome and covariate for two or more groups by evaluating whether the fitted regression curves differ significantly. When they do, researchers need to determine the "significance region," or the values of the covariate where the curves significantly differ. In analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), the Johnson-Neyman procedure can be used to determine the significance region; for the hierarchical linear model (HLM), the Miyazaki and Maier (M-M) procedure has been suggested. However, neither procedure can assume nonnormally distributed data. Furthermore, the M-M procedure produces biased (downward) results because it uses the Wald test, does not control the inflated Type I error rate due to multiple testing, and requires implementing multiple software packages to determine the significance region. In this article, we address these limitations by proposing solutions for determining the significance region suitable for generalized linear (mixed) model (GLM or GLMM). These proposed solutions incorporate test statistics that resolve the biased results, control the Type I error rate using Scheffé's method, and uses a single statistical software package to determine the significance region.
Keywords: generalized estimating equations; hierarchical linear models; longitudinal analysis; multiple testing; simultaneous testing.
Figures
References
-
- Coleman J, Hoffer T, Kilgore S. High school achievement: Public, Catholic, and other schools compared. New York, NY: Basic Books; 1982.
-
- Dempster AP, Rubin DB, Tsutakawa RK. Estimation in covariance components model. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 1981;76:341–353.
-
- Hunka S. Identifying regions of significance in ANCOVA problems having non-homogeneous regressions. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology. 1995;48:161–188.
-
- Hunka S, Leighton J. Defining Johnson-Neyman regions of significance in the three-covariate ANCOVA using Mathematica. Journal of Education and Behavioral Statistics. 1997;22:361–387.
-
- Johnson PO, Fay LC. The Johnson-Neyman technique, its theory and application. Psychometrika. 1950;15:349–367. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
