Caribbean maitotoxin elevates [Ca(2+)]i and activates non-selective cation channels in HIT-T15 cells
- PMID: 23772275
- PMCID: PMC3680626
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i3.70
Caribbean maitotoxin elevates [Ca(2+)]i and activates non-selective cation channels in HIT-T15 cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the cytotoxic mechanism of caribbean maitotoxin (MTX-C) in mammalian cells.
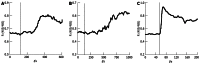
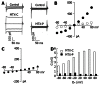
Methods: We used whole-cell patch-clamp techniques and fluorescence calcium imaging to determine the cellular toxic mechanisms of MTX-C in insulin secreting HIT-T15 cells, which is a system where the effects of MTX have been observed. HIT-T15 cells stably express L-type calcium current, making it a suitable model for this study. Using the fluorescence calcium indicator Indo-1 AM, we found that there is a profound increase in HIT-T15 intracellular free calcium 3 min after application of 200 nmol/L MTX-C.
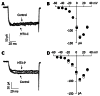
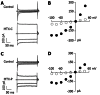
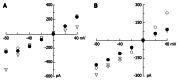
Results: About 3 min after perfusion of MTX-C, a gradual increase in free calcium concentration was observed. This elevation was sustained throughout the entire recording period. Application of MTX-C did not elicit the L-type calcium current, but large cationic currents appeared after applying MTX-C to the extracellular solution. The current-voltage relationship of the cation current is approximately linear within the voltage range from -60 to 50 mV, but flattened at voltages at -80 and -100 mV. These results indicate that MTX-C induces a non-voltage activated, inward current under normal physiological conditions, which by itself or through a secondary mechanism results in a large amount of cationic influx. The biophysical mechanism of MTX-C is different to its isoform, pacific maitotoxin (MTX-P), when the extracellular calcium is removed.
Conclusion: We conclude that MTX-C causes the opening of non-selective, non-voltage-activated ion channels, which elevates level of intracellular calcium concentration and leads to cellular toxicities.
Keywords: Calcium fluorescence; High voltage gated Ca2+ channels; Insulin secreting cells; Maitotoxin; Whole cell patch clamp.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maitotoxin induces insertion of different ion channels into the Xenopus oocyte plasma membrane via Ca(2+)-stimulated exocytosis.Pflugers Arch. 2000 Jan;439(3):363-9. doi: 10.1007/s004249900150. Pflugers Arch. 2000. PMID: 10650989
-
Studies on maitotoxin-induced intracellular Ca(2+) elevation in chinese hamster ovary cells stably transfected with cDNAs encoding for L-type Ca(2+) channel subunits.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Aug;290(2):725-30. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999. PMID: 10411584
-
Characterization of the maitotoxin-activated cationic current from human skin fibroblasts.J Physiol. 2002 Jan 1;538(Pt 1):79-86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013036. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11773318 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic agonists activate Ca2+ store-operated and -independent ionic currents in insulin-secreting HIT-T15 cells and mouse pancreatic beta-cells.J Membr Biol. 2004 Jan 1;197(1):59-70. doi: 10.1007/s00232-003-0642-y. J Membr Biol. 2004. PMID: 15014918
-
Maitotoxin (MTX) activates a nonselective cation channel in Xenopus laevis oocytes.Pflugers Arch. 1998 Aug;436(3):329-37. doi: 10.1007/PL00008085. Pflugers Arch. 1998. PMID: 9644213
Cited by
-
Emergent toxins in North Atlantic temperate waters: a challenge for monitoring programs and legislation.Toxins (Basel). 2015 Mar 16;7(3):859-85. doi: 10.3390/toxins7030859. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25785464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure Elucidation and Biological Evaluation of Maitotoxin-3, a Homologue of Gambierone, from Gambierdiscus belizeanus.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Feb 1;11(2):79. doi: 10.3390/toxins11020079. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30717108 Free PMC article.
-
Ladder-Shaped Ion Channel Ligands: Current State of Knowledge.Mar Drugs. 2017 Jul 20;15(7):232. doi: 10.3390/md15070232. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28726749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First Report of Ciguatoxins in Two Starfish Species: Ophidiaster ophidianus and Marthasterias glacialis.Toxins (Basel). 2015 Sep 21;7(9):3740-57. doi: 10.3390/toxins7093740. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26402702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takahashi M, Ohizumi Y, Yasumoto T. Maitotoxin, a Ca2+ channel activator candidate. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:7287–7289. - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama A, Murata M, Oshima Y, Iwashita T, Yasumoto T. Some chemical properties of maitotoxin, a putative calcium channel agonist isolated from a marine dinoflagellate. J Biochem. 1988;104:184–187. - PubMed
-
- Trevino S. Fish and shellfish poisoning. Clin Lab Sci. 1998;11:309–314. - PubMed
-
- Holmes MJ, Lewis RJ, Gillespie NC. Toxicity of Australian and French polynesian strains of Gambierdiscus toxicus (Dinophyceae) grown in culture: characterization of a new type of maitotoxin. Toxicon. 1990;28:1159–1172. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed FE. Seafood Safety. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 1991. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

