Irreversible inactivation of snake venom l-amino acid oxidase by covalent modification during catalysis of l-propargylglycine
- PMID: 23772385
- PMCID: PMC3668516
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fob.2013.01.010
Irreversible inactivation of snake venom l-amino acid oxidase by covalent modification during catalysis of l-propargylglycine
Abstract
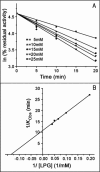
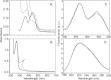
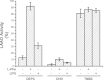
Snake venom l-amino acid oxidase (SV-LAAO, a flavor-enzyme) has attracted considerable attention due to its multifunctional nature, which is manifest in diverse clinical and biological effects such as inhibition of platelet aggregation, induction of cell apoptosis and cytotoxicity against various cells. The majority of these effects are mediated by H2O2 generated during the catalytic conversion of l-amino acids. The substrate analog l-propargylglycine (LPG) irreversibly inhibited the enzyme from Crotalus adamanteus and Crotalus atrox in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Inactivation was irreversible which was significantly protected by the substrate l-phenylalanine. A Kitz-Wilson replot of the inhibition kinetics suggested formation of reversible enzyme-LPG complex, which occurred prior to modification and inactivation of the enzyme. UV-visible and fluorescence spectra of the enzyme and the cofactor strongly suggested formation of covalent adduct between LPG and an active site residue of the enzyme. A molecular modeling study revealed that the FAD-binding, substrate-binding and the helical domains are conserved in SV-LAAOs and both His223 and Arg322 are the important active site residues that are likely to get modified by LPG. Chymotrypsin digest of the LPG inactivated enzyme followed by RP-HPLC and MALDI mass analysis identified His223 as the site of modification. The findings reported here contribute towards complete inactivation of SV-LAAO as a part of snake envenomation management.
Keywords: CHD, 1,2-cyclohexanedione; Crotalus adamanteus venom; Crotalus atrox venom; DEPC, diethylpyrocarbonate; FAD, flavin adenine dinucleotide; Gdn-HCl, guanidine hydrochloride; Irreversible inactivation; LAAO, l-amino acid oxidase (EC. 1.4.3.2); LPG, l-propargylglycine; MALDI-TOF, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight; Mechanism-based inhibitor; TNBS, trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.; l-Amino acid oxidase; l-Phe, l-phenylalaine; l-Propargylglycine.
Figures








References
-
- Curti B., Ronchi S., Simonetta M.P. D- and L-amino acid oxidases. In: Muller F., editor. vol. 3. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 1992. pp. 69–94. (In Chemistry and Biochemistry of Flavoenzymes).
-
- Du X.Y., Clemetson K.J. Snake venom L-amino acid oxidases. Toxicon. 2002;40:659–665. - PubMed
-
- Mandal S., Bhattacharyya D. Two L-amino acid oxidase isoenzymes from Russell's viper (Daboia russelli russelli) venom with different mechanism of inhibition by substrate analogs. FEBS J. 2008;275:2078–2095. - PubMed
-
- Fitzpatrick P.F. Carbanion versus hydride transfer mechanisms in flavoprotein-catalyzed dehydrogenations. Bioorg. Chem. 2004;32:125–139. - PubMed
-
- Sakurai Y., Takatsuka H., Yoshioka A., Matsui T., Suzuki M., Titani K., Fujimura Y. Inhibition of human platelet aggregation by L-amino acid oxidase purified from Naja naja kaouthia venom. Toxicon. 2001;39:1827–1833. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

