CYP3A activity in severe liver cirrhosis correlates with Child-Pugh and model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) scores
- PMID: 23772874
- PMCID: PMC3895357
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12182
CYP3A activity in severe liver cirrhosis correlates with Child-Pugh and model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) scores
Abstract
Aims: Impaired liver function often necessitates drug dose adjustment to avoid excessive drug accumulation and adverse events, but a marker for the extent of the required adjustment is lacking. The aim of this study was to investigate whether Child-Pugh (CP) and model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) scores correlate with drug clearance.
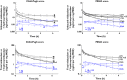
Methods: Midazolam was used as a CYP3A probe and its pharmacokinetics were analyzed in 24 patients with mild to severe liver cirrhosis (n = 4, 10 and 10 with CP class A, B and C, respectively) and six patients without liver disease.
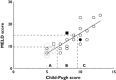
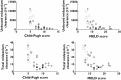
Results: Both scores correlated well with unbound midazolam clearance (CLu ), unbound midazolam fraction and half-life (all P < 0.01), whereas the unbound steady-state volume of distribution was not significantly changed. In patients with severe liver cirrhosis unbound midazolam clearance was only 14% of controls (CP C: CLu = 843 ± 346 l h(-1), MELD ≥ 15: CLu = 805 ± 474 l h(-1), controls: CLu = 5815 ± 2649 l h(-1), P < 0.01).
Conclusion: The correlation with unbound midazolam clearance suggests that either score predicts the metabolic capacity of CYP3A, the most relevant drug metabolizing enzyme subfamily in humans.
Keywords: Child-Pugh score; MELD score; cytochrome P450 CYP3A; liver cirrhosis; midazolam; pharmacokinetics.
© 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Verbeeck RK. Pharmacokinetics and dosage adjustment in patients with hepatic dysfunction. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;64:1147–1161. - PubMed
-
- Delcò F, Tchambaz L, Schlienger R, Drewe J, Krähenbühl S. Dose adjustment in patients with liver disease. Drug Saf. 2005;28:529–545. - PubMed
-
- Spray JW, Willett K, Chase D, Sindelar R, Connelly S. Dosage adjustment for hepatic dysfunction based on Child-Pugh scores. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64:690–693. - PubMed
-
- Amariles P, Lacampa P, Saez-Benito L. Dosage adjustments in hepatic dysfunction. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64:2536–2538. - PubMed
-
- Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for industry. Pharmacokinetics in patients with impaired hepatic function: study design, data analysis, and impact on dosing and labeling. May 2003. Available at http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformati... (last accessed 3 December 2012)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

