Necrosis predicts benefit from hypoxia-modifying therapy in patients with high risk bladder cancer enrolled in a phase III randomised trial
- PMID: 23773411
- PMCID: PMC3885794
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2013.05.017
Necrosis predicts benefit from hypoxia-modifying therapy in patients with high risk bladder cancer enrolled in a phase III randomised trial
Abstract
Background and purpose: Addition of carbogen and nicotinamide (hypoxia-modifying agents) to radiotherapy improves the survival of patients with high risk bladder cancer. The study investigated whether histopathological tumour features and putative hypoxia markers predicted benefit from hypoxia modification.
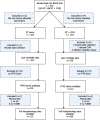
Materials and methods: Samples were available from 231 patients with high grade and invasive bladder carcinoma from the BCON phase III trial of radiotherapy (RT) alone or with carbogen and nicotinamide (RT+CON). Histopathological tumour features examined were: necrosis, growth pattern, growing margin, and tumour/stroma ratio. Hypoxia markers carbonic anhydrase-IX and glucose transporter-1 were examined using tissue microarrays.
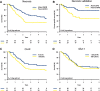
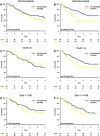
Results: Necrosis was the only independent prognostic indicator (P=0.04). Necrosis also predicted benefit from hypoxia modification. Five-year overall survival was 48% (RT) versus 39% (RT+CON) (P=0.32) in patients without necrosis and 34% (RT) versus 56% (RT+CON) (P=0.004) in patients with necrosis. There was a significant treatment by necrosis strata interaction (P=0.001 adjusted). Necrosis was an independent predictor of benefit from RT+CON versus RT (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.43, 95% CI 0.25-0.73, P=0.002). This trend was not observed when there was no necrosis (HR: 1.64, 95% CI 0.95-2.85, P=0.08).
Conclusions: Necrosis predicts benefit from hypoxia modification in patients with high risk bladder cancer and should be used to select patients; it is simple to identify and easy to incorporate into routine histopathological examination.
Keywords: Biomarker; Bladder cancer; Carbogen and nicotinamide; Hypoxic modification; Necrosis; Radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Grossman H.B., Natale R.B., Tangen C.M. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:859–866. - PubMed
-
- Dunst J., Rodel C., Zietman A., Schrott K.M., Sauer R., Shipley W.U. Bladder preservation in muscle-invasive bladder cancer by conservative surgery and radiochemotherapy. Semin Surg Oncol. 2001;20:24–32. - PubMed
-
- Rodel C., Grabenbauer G.G., Kuhn R. Combined-modality treatment and selective organ preservation in invasive bladder cancer: long-term results. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:3061–3071. - PubMed
-
- Hoskin P.J., Rojas A.M., Bentzen S.M., Saunders M.I. Radiotherapy with concurrent carbogen and nicotinamide in bladder carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4912–4918. - PubMed
-
- Overgaard J., Eriksen J.G., Nordsmark M., Alsner J., Horsman M.R. Plasma osteopontin, hypoxia, and response to the hypoxia sensitiser nimorazole in radiotherapy of head and neck cancer: results from the DAHANCA 5 randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:757–764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

