Perivenular brain lesions in a primate multiple sclerosis model at 7-tesla magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 23773983
- PMCID: PMC4745928
- DOI: 10.1177/1352458513492244
Perivenular brain lesions in a primate multiple sclerosis model at 7-tesla magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
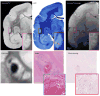
BACKGROUND Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide in vivo assessment of tissue damage, allowing evaluation of multiple sclerosis (MS) lesion evolution over time--a perspective not obtainable with postmortem histopathology. Relapsing-remitting experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an experimental model of MS that can be induced in the common marmoset, a small new world primate, and that causes perivenular white matter (WM) lesions similar to those observed in MS. METHODS Brain lesion development and evolution were studied in vivo and postmortem in four marmosets with EAE through serial T2- and T2*-weighted scans at 7-tesla. Supratentorial WM lesions were identified and characterized. RESULTS Of 97 lesions observed, 86 (88%) were clearly perivenular, and 62 (72%) developed around veins that were visible even prior to EAE induction. The perivenular configuration was confirmed by postmortem histopathology. Most affected veins, and their related perivascular Virchow-Robin spaces, passed into the subarachnoid space rather than the ventricles. CONCLUSION As in human MS, the intimate association between small veins and EAE lesions in the marmoset can be studied with serial in vivo MRI. This further strengthens the usefulness of this model for understanding the process of perivenular lesion development and accompanying tissue destruction in MS.
Keywords: Veins; experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; magnetic resonance imaging; multiple sclerosis; susceptibility weighted imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lucchinetti C, Bruck W, Parisi J, Scheithauer B, Rodriguez M, Lassmann H. Heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis lesions: implications for the pathogenesis of demyelination. Annals of neurology. 2000;47(6):707–17. Epub 2000/06/14. - PubMed
-
- Charcot JM. Histologie de la sclérose en plaques. Paris: Imprimerie L. Pupart-Davyl; 1869. p. 23.
-
- Tallantyre EC, Brookes MJ, Dixon JE, Morgan PS, Evangelou N, Morris PG. Demonstrating the perivascular distribution of MS lesions in vivo with 7-Tesla MRI. Neurology. 2008;70(22):2076–8. Epub 2008/05/29. - PubMed
-
- Adams CW. The onset and progression of the lesion in multiple sclerosis. Journal of the neurological sciences. 1975;25(2):165–82. Epub 1975/06/01. - PubMed
-
- Henderson AP, Barnett MH, Parratt JD, Prineas JW. Multiple sclerosis: distribution of inflammatory cells in newly forming lesions. Ann Neurol. 2009;66(6):739–53. Epub 2009/12/26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

