Building unique bonds to fight misplaced DNA
- PMID: 23774266
- PMCID: PMC3760622
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2013.81
Building unique bonds to fight misplaced DNA
Abstract
A cyclic dinucleotide comprised of GMP and AMP was previously shown to be a key intermediate during activation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA. A report by Patel and Tuschl groups published in Cell reveals the structure of the enzyme involved in the synthesis of this second messenger and identifies this cyclic dinucleotide as a unique compound in metazoan cell signaling.
Figures
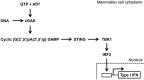
Comment on
-
Cyclic [G(2',5')pA(3',5')p] is the metazoan second messenger produced by DNA-activated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase.Cell. 2013 May 23;153(5):1094-107. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.046. Epub 2013 May 3. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23647843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Neill LA. Science. 2013. pp. 763–764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

