Evaluation of initial and steady-state gatifloxacin pharmacokinetics and dose in pulmonary tuberculosis patients by using monte carlo simulations
- PMID: 23774436
- PMCID: PMC3754315
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00479-13
Evaluation of initial and steady-state gatifloxacin pharmacokinetics and dose in pulmonary tuberculosis patients by using monte carlo simulations
Abstract
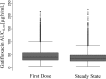
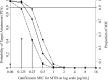
A 4-month regimen of gatifloxacin with rifampin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide is being evaluated for the treatment of tuberculosis in a phase 3 randomized controlled trial (OFLOTUB). A prior single-dose study found that gatifloxacin exposure increased by 14% in the combination. The aims of the study are to evaluate the initial and steady-state pharmacokinetics of gatifloxacin when daily doses are given to patients with newly diagnosed drug-sensitive pulmonary tuberculosis as part of a combination regimen and to evaluate the gatifloxacin dose with respect to the probability of attaining a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic target. We describe the population pharmacokinetics of gatifloxacin from the first dose to a median of 28 days in 169 adults enrolled in the OFLOTUB trial in Benin, Guinea, Senegal, and South Africa. The probability of achieving a ratio of ≥125 for the area under the concentration time curve to infinity (AUC0-∞) for the free fraction of gatifloxacin over the MIC (fAUC/MIC) was investigated using Monte Carlo simulations. The median AUC0-∞ of 41.2 μg · h/ml decreased on average by 14.3% (90% confidence interval [CI], -90.5% to +61.5%) following multiple 400-mg daily doses. At steady state, 90% of patients achieved an fAUC/MIC of ≥125 only when the MIC was <0.125 μg/ml. We conclude that systemic exposure to gatifloxacin declines with repeated daily 400-mg doses when used together with rifampin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide, thus compensating for any initial increase in gatifloxacin levels due to a drug interaction. (The OFLOTUB study has been registered at ClinicalTrials.gov under registration no. NCT00216385.).
Figures


References
-
- Rodriguez JC, Ruiz M, Lopez M, Royo G. 2002. In vitro activity of moxifloxacin, levofloxacin, gatifloxacin and linezolid against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 20:464–467 - PubMed
-
- Singh M, Chauhan DS, Gupta P, Das R, Srivastava RK, Singh PUP, Srivastava K, Faujdar J, Jaudaun GPS, Yadav VS, Sharma VD, Venkatesan K, Sachan S, Sachan P, Katoch K, Katoch VM. 2009. In vitro effect of fluoroquinolones against Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from Agra & Kanpur region of north India. Indian J. Med. Res. 129:542–547 - PubMed
-
- Cynamon MH, Sklaney MR, Shoen C. 2007. Gatifloxacin in combination with rifampicin in a murine tuberculosis model. J. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60:429–432 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

