Human chorionic gonadotropin beta subunit genes CGB1 and CGB2 are transcriptionally active in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 23774837
- PMCID: PMC3709805
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140612650
Human chorionic gonadotropin beta subunit genes CGB1 and CGB2 are transcriptionally active in ovarian cancer
Abstract
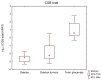
Human chorionic gonadotropin beta subunit (CGB) is a marker of pregnancy as well as trophoblastic and nontrophoblastic tumors. CGB is encoded by a cluster of six genes, of which type II genes (CGB3/9, 5 and 8) have been shown to be upregulated in relation to type I genes (CGB6/7) in both placentas and tumors. Recent studies revealed that CGB1 and CGB2, originally considered as pseudogenes, might also be active, however, the protein products of these genes have not yet been identified. Our study demonstrates the presence of CGB1 and CGB2 transcripts in ovarian carcinomas. While CGB1 and CGB2 gene activation was not detected in normal ovaries lacking cancerous development, our study demonstrates the presence of CGB1 and CGB2 transcripts in 41% of analyzed ovarian cancer cases.
Figures



References
-
- Pierce J.G., Parsons T.F. Glycoprotein hormones: Structure and function. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1981;50:465–495. - PubMed
-
- Iles R.K. Ectopic hCGbeta expression by epithelial cancer: malignant behaviour, metastasis and inhibition of tumor cell apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007;260–262:264–270. - PubMed
-
- Vartiainen J., Lehtovirta P., Finne P., Stenman U.H., Alfthan H. Preoperative serum concentration of hCGbeta as a prognostic factor in ovarian cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 2001;95:313–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

