Prevalence of hypertension in china: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 23776574
- PMCID: PMC3679057
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065938
Prevalence of hypertension in china: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Aims: The present study aimed to assess the prevalence of hypertension among Chinese adults.
Methods: Data were obtained from sphygmomanometer measurements and a questionnaire administered to 46239 Chinese adults ≥20 years of age who participated in the 2007-2008 China National Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders Study. Hypertension was defined as blood pressure ≥140/90 mm Hg or use of antihypertensive medication.
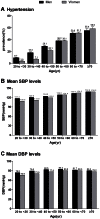
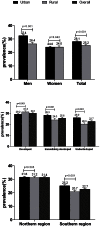
Results: A total of 26.6% of Chinese adults had hypertension, and a significantly greater number of men were hypertensive than women (29.2% vs 24.1%, p<0.001). The age-specific prevalence of hypertension was 13.0%, 36.7%, and 56.5% among persons aged 20 to 44 years (young people), 45 to 64 years (middle-aged people), and ≥65 years (elderly people), respectively. In economically developed regions, the prevalence of hypertension was significantly higher among rural residents than among urban residents (31.3% vs 29.2%, p = 0.001). Among women or individuals who lived in the northern region, the disparity in the prevalence of hypertension between urban and rural areas disappeared (women: 24.0% vs. 24.0%, p = 0.942; northern region: 31.6% vs. 31.2%, p = 0.505). Among hypertensive patients, 45.0% were aware of their condition, 36.2% were treated, and 11.1% were adequately controlled.
Conclusions: The prevalence of hypertension in China is increasing. The trend of an increase in prevalence is striking in young people and rural populations. Hypertension awareness, treatment, and control are poor. Public health efforts for further improving awareness and enhancing effective control are urgently needed in China, especially in emerging populations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- He J, Gu D, Wu X, Reynolds K, Duan X, et al. (2005) Major causes of death among men and women in China. N Engl J Med 353: 1124–1134. - PubMed
-
- Messerli FH, Williams B, Ritz E (2007) Essential hypertension. Lancet 370: 591–603. - PubMed
-
- Dahlof B (2007) Prevention of stroke in patients with hypertension. Am J Cardiol 100: 17J–24J. - PubMed
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, et al. (2005) Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 365: 217–223. - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Duan X, Gu D, Hao J, Tao S, et al. (1995) Prevalence of hypertension and its trends in Chinese populations. Int J Cardiol 52: 39–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

