Characterization of incidental liver lesions: comparison of multidetector CT versus Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging
- PMID: 23776623
- PMCID: PMC3679037
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066141
Characterization of incidental liver lesions: comparison of multidetector CT versus Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(10). doi:10.1371/annotation/a03efa25-49f8-4616-a256-074a3d60ceaf
Abstract
As a result of recent developments in imaging modalities and wide spread routine medical checkups and screening, more incidental liver lesions are found frequently on US these days. When incidental liver lesions are found on US, physicians have to make a decision whether to just follow up or to undergo additional imaging studies for lesion characterization. In order to choose the next appropriate imaging modality, the diagnostic accuracy of each imaging study needs to be considered. Therefore, we tried to compare the accuracy of contrast-enhanced multidetector CT (MDCT) and Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI for characterization of incidental liver masses. We included 127 incidentally found focal liver lesions (94 benign and 33 malignant) from 80 patients (M∶F = 45∶35) without primary extrahepatic malignancy or chronic liver disease. Two radiologists independently reviewed Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI and MDCT. The proportion of confident interpretations for differentiation of benign and malignant lesions and for the specific diagnosis of diseases were compared. The proportion of confident interpretations for the differentiation of benign and malignant lesions was significantly higher with EOB-MRI(94.5%-97.6%) than with MDCT (74.0%-92.9%). In terms of specific diagnosis, sensitivity and accuracy were significantly higher with EOB-MRI than with MDCT for the diagnosis of focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) and focal eosinophilic infiltration. The diagnoses of the remaining diseases were comparable between EOB-MRI and MDCT. Hence, our results suggested that Gd-EOB-MRI may provide a higher proportion of confident interpretations than MDCT, especially for the diagnosis of incidentally found FNH and focal eosinophilic infiltration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

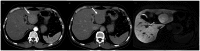
References
-
- Gore RM, Newmark GM, Thakrar KH, Mehta UK, Berlin JW (2011) Hepatic incidentalomas. Radiol Clin North Am 49: 291–322. - PubMed
-
- Boutros C, Katz SC, Espat NJ (2010) Management of an incidental liver mass. Surg Clin North Am 90: 699–718. - PubMed
-
- Furtado CD, Aguirre DA, Sirlin CB, Dang D, Stamato SK, et al. (2005) Whole-body CT screening: spectrum of findings and recommendations in 1192 patients. Radiology 237: 385–394. - PubMed
-
- Soussan M, Aube C, Bahrami S, Boursier J, Valla DC, et al. (2010) Incidental focal solid liver lesions: diagnostic performance of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and MR imaging. Eur Radiol 20: 1715–1725. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

